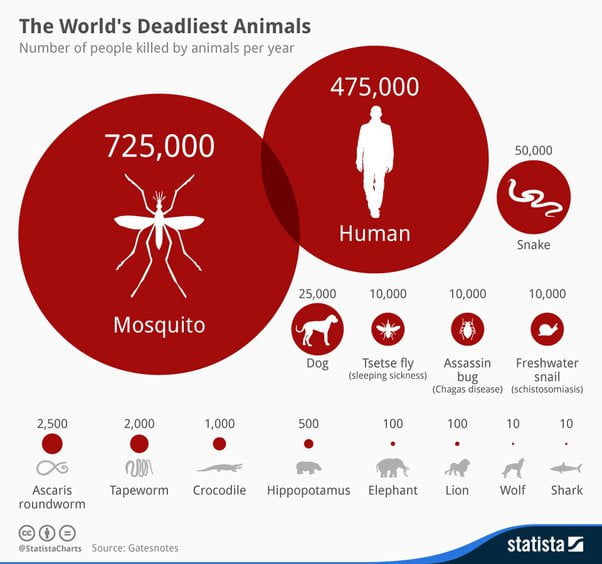
Mosquitoes have killed over one million people worldwide due to mosquito-borne diseases annually. These tiny insects are responsible for causing significant human suffering and fatalities.
Mosquito-borne illnesses such as malaria, dengue fever, Zika virus, and yellow fever are prevalent in many parts of the world, leading to high mortality rates. Despite their small size, mosquitoes pose a massive threat to global health and continue to claim numerous lives each year.
Efforts to control mosquito populations and prevent the spread of diseases remain crucial in combating this deadly menace.

Credit: www.realclearscience.com
Mosquitoes: The Silent Killers
Death Toll Through The Ages
The death toll caused by mosquitoes throughout history is staggering. Mosquito-borne diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus have claimed countless lives. According to the World Health Organization, malaria alone has been responsible for an estimated 228 million cases and 405,000 deaths in 2018. These statistics underscore the devastating impact of mosquito-borne illnesses on global health.
Comparing Mosquito Fatalities To Wars
When comparing mosquito fatalities to the death tolls of wars, the numbers are astonishing. While specific data on the total number of people killed by mosquitoes is challenging to quantify, it is believed that the cumulative death toll from mosquito-borne diseases far exceeds the casualties of all wars in history. This grim reality highlights the urgent need for continued efforts to combat and control mosquito populations.
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/18968476/mosquito_mankind.jpg)
Credit: www.vox.com
Deadliest Species On The Planet
Mosquitoes are the deadliest species on the planet, killing over one million people worldwide each year through the transmission of diseases such as malaria, dengue, and Zika. This makes mosquitoes deadlier than all the wars in history combined, highlighting the significant impact of these tiny but deadly insects on human populations.
Species With The Highest Kill Counts
Mosquitoes, particularly the Anopheles, Aedes, and Culex species, are responsible for the most human deaths worldwide.
Geographical Hotspots For Fatalities
Regions like Sub-Saharan Africa, Southeast Asia, and South America are hotspots for mosquito-related fatalities.
Disease And Death: A Mosquito’s Legacy
Mosquitoes have caused over one million deaths worldwide annually from mosquito-borne diseases. They are considered more deadly to humans than any other organism, making them a significant global health threat.
Malaria’s Grim Statistics
Malaria is one of the most deadly diseases spread by mosquitoes, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, where most of the deaths occur. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), in 2019, there were an estimated 229 million cases of malaria worldwide, with 409,000 deaths. Children under the age of 5 are the most vulnerable, with one child dying every two minutes from malaria.Other Deadly Diseases Spread By Mosquitoes
Malaria is not the only deadly disease transmitted by mosquitoes. Other diseases include dengue fever, Zika virus, chikungunya, yellow fever, and West Nile virus. In the United States, West Nile virus is the most common mosquito-borne disease, with an average of 2,000 cases reported each year.It is estimated that mosquitoes are responsible for over one million deaths each year worldwide. This makes them one of the deadliest animals on the planet. In fact, mosquitoes have killed more humans than all the wars in history combined.Mosquitoes have been around for millions of years and have developed a reputation for being relentless bloodsuckers. While their bites are annoying and itchy, the real danger lies in the diseases they transmit. Despite efforts to control their populations, mosquitoes continue to pose a significant threat to public health.Annual Casualties: A Yearly Analysis
Mosquitoes are not just a nuisance, but also a deadly threat, causing a significant number of deaths each year. It is crucial to analyze the yearly casualties caused by mosquito-borne diseases to understand the severity of the situation and to implement effective preventive measures.
Tracking Yearly Death Rates
The annual death toll due to mosquito-borne diseases is alarming. According to the World Health Organization, over one million people worldwide succumb to these diseases every year. This staggering number underscores the urgent need for robust mosquito control and public health measures.
Trends In Mosquito-borne Disease Mortality
Examining the trends in mosquito-borne disease mortality reveals fluctuating patterns influenced by various factors such as climate change, urbanization, and global travel. Understanding these trends is crucial for developing targeted interventions and allocating resources to combat these diseases effectively.
The Global Impact Of Mosquitoes
Effects On Public Health
Mosquitoes cause more human suffering than any other organism. Over one million people worldwide die from mosquito-borne diseases every year, making mosquitoes the world’s deadliest animal. Mosquito-borne diseases such as West Nile Virus, Dengue, and Chikungunya Virus contribute significantly to the global burden of disease, impacting public health on a massive scale.
Economic Consequences Of Mosquito-borne Diseases
The economic impact of mosquito-borne diseases is substantial. The financial burden of treating these diseases, loss of productivity due to illness, and the costs associated with mosquito control efforts place a heavy strain on healthcare systems and economies worldwide. Additionally, countries with high mosquito-borne disease prevalence often experience reduced tourism and foreign investment, further exacerbating the economic consequences.

Credit: www.cbsnews.com
Mosquito Control: Measures And Challenges
Mosquito control measures are crucial due to the staggering toll mosquitoes take on human lives worldwide. Over one million people die annually from mosquito-borne diseases, making mosquitoes deadlier than many historical wars combined. The challenges lie in effectively combating these disease-carrying pests to reduce the human impact.
Mosquitoes are one of the deadliest animals in the world, responsible for more human deaths than any other organism. Mosquito-borne diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus have been a major public health concern for decades. The global efforts to control mosquito populations have made significant progress, but there are still many challenges that need to be addressed.Success Stories In Mosquito Eradication
There have been several success stories in mosquito eradication, such as the elimination of malaria from many countries in Europe and North America. In addition, the use of insecticide-treated bed nets and indoor residual spraying has been effective in reducing malaria transmission in many African countries. The use of genetically modified mosquitoes that are unable to transmit diseases is also being explored as a potential solution.Controversies And Consequences Of Control Methods
Despite the success stories, there are controversies surrounding some of the control methods. The use of insecticides has led to the development of insecticide-resistant mosquitoes, and there are concerns about the environmental impact of some of the chemicals used. In addition, the release of genetically modified mosquitoes has raised ethical concerns and the potential for unintended consequences.In conclusion, mosquito control measures have been successful in reducing the burden of mosquito-borne diseases, but there are still many challenges that need to be addressed. The use of innovative and sustainable methods is necessary to achieve long-term success in mosquito control and eradication.The Environmental Role Of Mosquitoes
Mosquitoes play a crucial environmental role, but they are also responsible for over one million human deaths annually due to mosquito-borne diseases worldwide. These tiny insects have tragically claimed more lives than all the wars in history combined.
Ecosystem Contributions
Mosquitoes play a vital role in the ecosystem, serving as a food source for various animals such as birds, fish, and bats. They also contribute to pollination and nutrient cycling.Hypotheticals: A World Without Mosquitoes
If mosquitoes were eradicated, the food chain would be disrupted, leading to population imbalances among species that rely on them for sustenance. Additionally, the absence of mosquitoes could impact plant pollination and nutrient distribution.Prevention And Protection Strategies
Mosquitoes are notorious for spreading deadly diseases, resulting in millions of deaths worldwide. However, by implementing effective prevention and protection strategies, individuals and communities can minimize the risk of mosquito-borne illnesses.
Advancements In Mosquito Repellents
In recent years, significant advancements have been made in mosquito repellent technology. Innovative formulations and application methods have enhanced the effectiveness and longevity of repellents, providing long-lasting protection against mosquito bites.
Furthermore, the development of natural and eco-friendly repellents offers a safer alternative for individuals concerned about the potential health risks associated with chemical-based products. These advancements empower individuals to choose from a diverse range of repellent options, catering to their specific preferences and needs.
Community Initiatives To Reduce Risk
Community-driven efforts play a crucial role in reducing the prevalence of mosquitoes and mitigating the associated health risks. Collaborative initiatives such as environmental clean-up campaigns and waste management programs contribute to the elimination of mosquito breeding sites, thereby reducing their population.
Moreover, public awareness and education programs empower communities to implement preventive measures and recognize the symptoms of mosquito-borne diseases, enabling early detection and treatment. By fostering a collective commitment to mosquito control and disease prevention, communities can significantly reduce the impact of these deadly insects.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Many People Have Mosquitos Killed?
Mosquitoes have killed over one million people worldwide annually due to mosquito-borne diseases.
Have Mosquitoes Killed More Humans Than All The Wars In History?
Yes, mosquitoes have killed more humans than all the wars in history combined.
What Happened If We Killed All Mosquitoes?
If we killed all mosquitoes, it could stop disease spread, but may disrupt the environment, affecting animals and plants.
Conclusion
Mosquitoes, the stealthy killers, have claimed over a million lives annually worldwide. Eradicating them may halt diseases but could disrupt ecosystems. Consider the balance before taking action. Understanding their impact is crucial for effective control measures. Stay informed, stay safe.
Related posts:

I’m MD Tanvir, and I bring years of expertise gained from working closely with pest control companies to the forefront. My journey in the industry has inspired me to launch Bug Battler, a platform aimed at equipping people with the know-how to combat pests autonomously. Through Bug Battler, I aim to empower individuals with practical insights to tackle pest infestations effectively.