Mosquitoes have caused over 700 million deaths in history, primarily due to diseases like malaria. This staggering number highlights the deadly impact of these tiny insects.
Mosquito-borne diseases have plagued human societies for centuries, leading to widespread suffering and loss of life. Malaria alone has been responsible for a significant portion of these fatalities. The prevalence of mosquito-borne illnesses underscores the urgent need for effective preventive measures and treatments.
Understanding the historical toll of mosquito-related deaths can inform current efforts to combat these diseases and minimize their impact on global health.
The Mosquito: A Lethal Force In Human History
Throughout history, the tiny mosquito has posed a significant threat to human life, often underestimated for its lethal potential. The impact of mosquito-borne diseases has been felt across civilizations, causing widespread suffering and fatalities. Examining the historical instances of mosquito-borne disease outbreaks sheds light on the devastating impact of these tiny predators on human populations.
The Underestimated Danger Of The Tiny Predator
Despite its diminutive size, the mosquito has been responsible for causing more human suffering and death than any other organism. This deadly vector transmits a range of diseases, including malaria, dengue fever, yellow fever, and Zika virus, claiming over one million lives annually. The underestimated danger of these tiny predators becomes evident when considering the staggering toll of mosquito-borne illnesses on global health.
Historical Instances Of Mosquito-borne Disease Outbreaks
Throughout history, mosquito-borne diseases have left a trail of devastation in their wake. From the ancient civilizations of Egypt and Rome to the exploration and colonization of the Americas, outbreaks of malaria and other mosquito-borne illnesses have shaped the course of human history. The toll of these diseases on military campaigns, trade routes, and the development of nations underscores the profound historical impact of mosquito-borne diseases.
Quantifying The Death Toll
Estimating Fatalities Throughout The Ages
Mosquitoes, often considered the world’s deadliest creatures, have been responsible for an astonishing number of deaths throughout history. Estimating the exact number of fatalities is a challenging task, given the wide range of diseases transmitted by these tiny but formidable insects.
Malaria, dengue fever, yellow fever, and other mosquito-borne illnesses have claimed the lives of millions over the centuries. The lack of precise records and the prevalence of these diseases in regions with limited access to healthcare further complicate efforts to quantify the death toll caused by mosquitoes.
Challenges In Tracking Mosquito-related Deaths
Accurately tracking mosquito-related deaths presents several challenges. Many fatalities occurred in ancient times and were not documented systematically. Additionally, the symptoms of mosquito-borne diseases often resemble those of other illnesses, leading to potential misdiagnoses and underreporting.
Furthermore, in regions with high mosquito-borne disease burden, accurate record-keeping and reporting infrastructure may be lacking, making it difficult to capture the full extent of the impact of these diseases on human populations.
Malaria’s Deadly Grip On Humanity
Throughout history, mosquitoes have claimed countless lives through deadly diseases like malaria. The death toll from mosquito-borne illnesses surpasses casualties from all wars combined.
The Role Of Malaria In Human Mortality
Malaria is one of the deadliest diseases in human history, responsible for countless deaths throughout the ages. It is caused by parasites transmitted through the bites of infected mosquitoes, primarily the Anopheles mosquito. While malaria can be treated with drugs, the disease remains a major public health problem in many parts of the world, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa.Epidemiological Impact Of Malaria Historically
Malaria has had a profound impact on human history, causing widespread illness and death in many parts of the world. It is estimated that malaria has killed more people throughout history than any other disease, including all wars and other disasters combined. In fact, some estimates suggest that malaria may have been responsible for half of all human deaths since the beginning of recorded history.Despite its devastating impact, malaria has also played a significant role in shaping human history. For example, the disease is thought to have contributed to the decline of the Roman Empire and the conquest of Africa by European colonial powers. In addition, efforts to control and prevent malaria have led to significant advances in medicine and public health.In conclusion, malaria’s deadly grip on humanity has been felt throughout history, causing untold suffering and death. While progress has been made in controlling the disease, much work remains to be done in order to eliminate malaria as a public health threat.
Credit: www.vox.com
Other Mosquito-borne Diseases And Their Impact
Mosquito-borne diseases, such as malaria, dengue, and yellow fever, have caused millions of deaths throughout history. Over one million people worldwide succumb to these diseases annually, with additional tens of millions suffering from debilitating effects. The impact of mosquito-borne illnesses is profound and continues to pose a significant threat to global health.
Yellow Fever
Yellow fever, transmitted by infected mosquitoes, has plagued populations for centuries. It has caused devastating outbreaks in Africa and the Americas, leading to high mortality rates.Dengue
Dengue fever, another mosquito-borne illness, affects millions globally. It can result in severe flu-like symptoms and, in some cases, progress to a life-threatening condition known as dengue hemorrhagic fever.Encephalitis
Mosquito-borne encephalitis viruses, such as West Nile virus and Japanese encephalitis virus, can cause inflammation of the brain. These diseases have significant health implications and can lead to long-term neurological complications.| Mosquito-Borne Disease | Global Health Implications |
|---|---|
| Yellow Fever | High mortality rates in Africa and the Americas |
| Dengue | Millions affected worldwide with potential life-threatening complications |
| Encephalitis | Brain inflammation leading to neurological complications |
- Yellow fever, dengue, and encephalitis are just a few examples of the devastating impact of mosquito-borne diseases on global health.
- These illnesses have caused widespread suffering and mortality, particularly in regions where mosquitoes thrive.
Comparing Mosquito Fatalities To Human Conflicts
When it comes to assessing the impact of mosquitoes on human history, a startling comparison emerges when we pit the fatalities caused by these tiny insects against the death toll of human conflicts. Mosquitoes, often underestimated, have proven to be a formidable foe, claiming an astonishing number of lives throughout history.
Mosquitoes Vs. Wars: A Death Toll Comparison
Mosquitoes cause more human suffering than any other organism, with over one million people worldwide succumbing to mosquito-borne diseases annually. In contrast, the death toll of human conflicts, while significant, pales in comparison to the silent but deadly impact of mosquitoes.
The Insidious Nature Of Mosquito-borne Disease Warfare
Mosquitoes have been waging a stealthy war on humanity through the transmission of diseases such as malaria, dengue, yellow fever, and Zika virus. These diseases, often fatal if left untreated, have claimed countless lives throughout history, silently ravaging populations across the globe.
Ecosystem And Mosquitoes: An Intricate Balance
Throughout history, mosquitoes have caused more human deaths than all the wars combined, with over one million people dying annually from mosquito-borne diseases. This intricate balance in the ecosystem underscores the critical role of mosquitoes and the devastating impact they have had on human populations.
The Role Of Mosquitoes In Ecosystems
Mosquitoes are often seen as a nuisance to humans due to their annoying bites and ability to transmit deadly diseases. However, they play a crucial role in many ecosystems as a food source for other animals. Mosquito larvae are an important food source for fish, frogs, and birds, and adult mosquitoes are eaten by bats, spiders, and other insects. Without mosquitoes, many of these animals would struggle to find enough food to survive.Consequences Of A World Without Mosquitoes
While it might be tempting to imagine a world without mosquitoes, the consequences of their absence could be devastating. As mentioned earlier, many animals rely on mosquitoes as a food source. Without mosquitoes, these animals would have to find other sources of food, which could lead to a decline in their populations. Additionally, mosquitoes play a role in pollinating plants and breaking down organic matter in bodies of water. Without them, these important ecological processes could be disrupted.Overall, while mosquitoes may be a nuisance to humans, they play a vital role in many ecosystems. It is important to find ways to control mosquito populations without completely eradicating them, in order to maintain the delicate balance of our planet’s ecosystems.Modern Strategies In Mosquito Control And Disease Prevention
Modern Strategies in Mosquito Control and Disease Prevention have significantly evolved over the years, with advancements in technologies and public health initiatives playing a crucial role in combating mosquito-borne diseases.
Advancements In Mosquito Control Technologies
The development of innovative technologies has revolutionized mosquito control efforts. Genetic modification of mosquitoes, including the use of Wolbachia bacteria to reduce their ability to transmit diseases, has shown promising results. Larvicides and insect growth regulators are being used to target mosquito larvae, while ultrasonic devices and mosquito traps provide non-toxic methods for controlling adult mosquito populations.
Public Health Initiatives In Combating Mosquito-borne Diseases
Public health initiatives are pivotal in preventing and managing mosquito-borne diseases. Community education campaigns raise awareness about the importance of eliminating breeding sites and using insect repellents. Integrated vector management programs focus on environmental modifications to reduce mosquito habitats, alongside surveillance and monitoring efforts to track disease transmission. Additionally, vaccination programs for diseases like malaria and dengue are essential in high-risk regions.
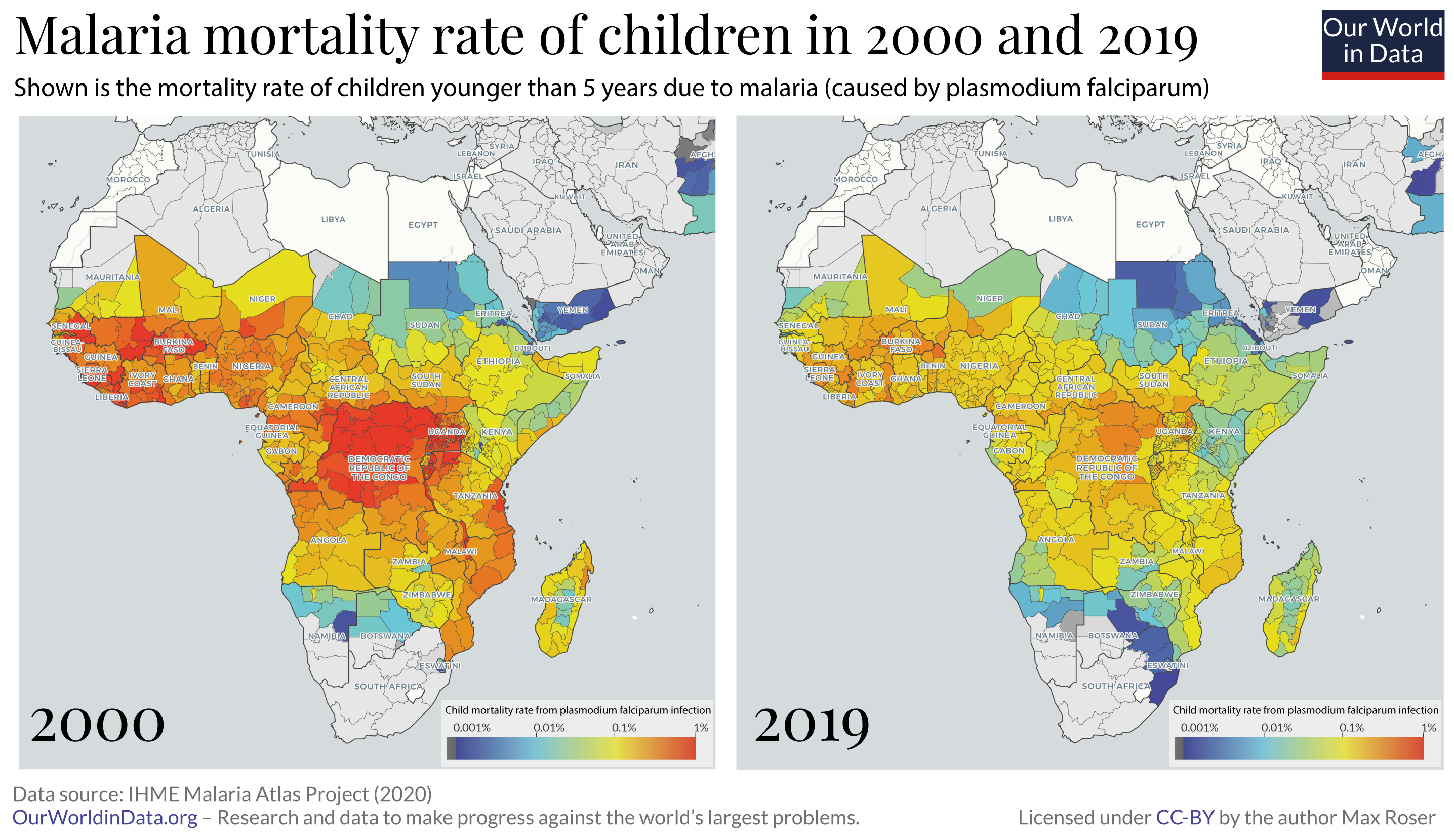
Credit: ourworldindata.org
Future Projections And Research
The Ongoing Battle Against Mosquito-transmitted Diseases
The fight against mosquito-borne diseases continues to be a critical global health challenge. Mosquitoes are responsible for transmitting a wide range of deadly illnesses, including malaria, dengue fever, Zika virus, and yellow fever. These diseases have claimed countless lives throughout history, particularly in regions with limited access to healthcare and resources.
Innovative Research And Potential Breakthroughs
Ongoing research efforts are focused on developing innovative strategies to combat mosquito-transmitted diseases. Scientists and researchers are exploring cutting-edge technologies such as genetic modification and advanced insecticides to target mosquito populations. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on public health interventions, including community education and the use of mosquito nets and repellents to reduce exposure to these deadly vectors.
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/18968476/mosquito_mankind.jpg)
Credit: www.vox.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Have Mosquitoes Killed More Humans Than All The Wars In History?
Yes, mosquitoes have killed more humans than all the wars in history combined.
How Many Have Died From Malaria In History?
Over one million people worldwide have died from malaria throughout history.
What Is The Deadliest Mosquito?
The deadliest mosquito is the Anopheles mosquito, responsible for transmitting malaria, causing over one million deaths annually worldwide.
Conclusion
Mosquitoes have been responsible for countless deaths throughout history. Their impact on human health cannot be underestimated. It is crucial to continue efforts in mosquito control and prevention to reduce the devastating effects of mosquito-borne diseases globally.
Related posts:

I’m MD Tanvir, and I bring years of expertise gained from working closely with pest control companies to the forefront. My journey in the industry has inspired me to launch Bug Battler, a platform aimed at equipping people with the know-how to combat pests autonomously. Through Bug Battler, I aim to empower individuals with practical insights to tackle pest infestations effectively.