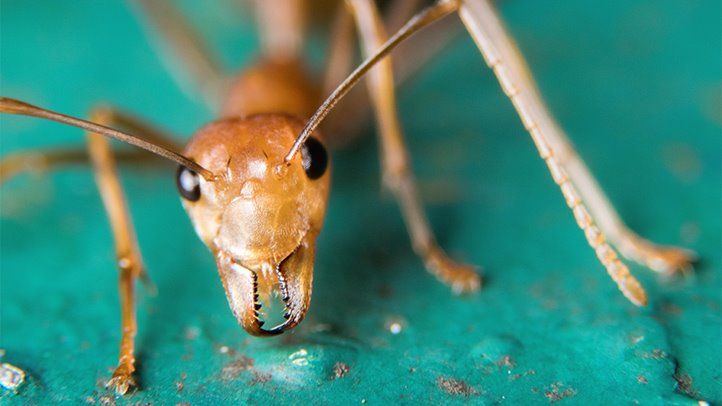
Ants bite as a defense mechanism or to protect their territory. When disturbed, they release pheromones and bite to defend themselves and their colony.
Ant bites are often painful and can cause irritation, redness, and swelling due to the venom injected by the ant. Ant bites can be a nuisance and cause discomfort, especially for individuals allergic to insect venom. Understanding why ants bite can help people take necessary precautions when dealing with ants in their environment.
By being aware of the reasons behind ant bites, individuals can better protect themselves and effectively manage ant infestations in their surroundings.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/FireAntBite-9f9561b55155424b997d2bbb6cbccc7a.jpg)
Credit: www.health.com
The Science Behind Ant Bites
Ant bites can be a real nuisance, causing painful swelling and itching. But have you ever wondered why ants bite in the first place? The answer lies in the science behind ant bites. These tiny creatures have evolved unique adaptations and physiological structures that allow them to deliver a potent bite. In this article, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of ants and explore the anatomy of their bite as well as the chemicals found in ant venom.
Anatomy Of Ant’s Bite
Ant anatomy plays a crucial role in their ability to deliver bites. The mouthparts of an ant consist of powerful mandibles that act as formidable cutting tools. These mandibles are used not only for feeding but also for defense and communication. When an ant bites, its mandibles clamp down on the victim’s skin, breaking the surface and allowing access to the underlying tissues.
This initial bite is often followed by a series of stings, where the ant injects venom into the wound. This venom contains potent substances that can cause a range of effects, from pain and irritation to allergic reactions in some individuals. Understanding the chemicals found in ant venom can provide further insights into the reasons behind their biting behavior.
Chemicals In Ant Venom
Ants produce and release venom as a defense mechanism. This venom contains a complex mixture of chemicals, each with its specific functions. One of the primary components found in ant venom is formic acid, a substance that gives ants their characteristic acidic odor. Formic acid helps to immobilize or kill prey, acting as a powerful deterrent against potential threats.
In addition to formic acid, ant venom may also contain alkaloids, peptides, and proteins, which can elicit various physiological responses in both insects and mammals. These compounds can cause pain, inflammation, and itching when they come into contact with human skin. Some ants, such as fire ants, even have venom that can cause severe allergic reactions in susceptible individuals.
It’s important to note that ant bites are not always aggressive. Some ants may bite when they feel threatened or when their nests are disturbed. Understanding the science behind ant bites can help us avoid unwanted encounters and develop effective strategies for ant control.
Types Of Ants That Bite
Fire Ants
Fire ants are notorious for their painful bites and aggressive behavior. These reddish-brown ants are known for their large, conspicuous mounds and are commonly found in the southern United States. When disturbed, fire ants will swarm and deliver painful stings, often leaving itchy, red welts on the skin. Avoiding their mounds and wearing protective clothing can help prevent painful encounters with fire ants.
Bullet Ants
Bullet ants, named for the intense pain of their sting which is said to be as painful as being shot with a bullet, are found in Central and South America. These large, black ants are known for their potent venom and aggressive nature. Encountering a bullet ant can lead to excruciating pain, swelling, and even fever. Avoiding their habitats and wearing protective gear is crucial when exploring regions where bullet ants are present.
Reasons Why Ants Bite
Ants bite for defensive purposes, to protect their territory, locate food, or communicate with other ants. They release formic acid, which can cause irritation or pain when they bite. Additionally, some ants may bite when they feel threatened, and certain species can release pheromones to signal others to attack.
Reasons Why Ants BiteAnts are known for their painful bites, and there are several reasons why they engage in this behavior. Understanding the reasons behind ant bites can help us better coexist with these fascinating insects. Let’s delve into the factors that drive ants to bite.Defense MechanismAnts primarily bite as a defense mechanism to protect themselves, their colony, and the queen. When they sense a threat, such as a human disturbing their nest or picking them up, they use their powerful mandibles to bite and hold onto the perceived intruder. This biting behavior serves as a warning to potential attackers and deters them from further disturbing the ant colony.Foraging and FeedingAnother reason why ants bite is related to foraging and feeding. As they gather food and resources, ants may encounter obstacles or competitors, such as other insects or even larger animals. In these situations, they use their biting capability to defend their food sources and ensure the survival of their colony. Additionally, ants may resort to biting as a means of obtaining nutrients from larger prey or defending themselves against predators while foraging.Furthermore, ants also bite as a way to communicate and interact with members of their own colony. Through the use of pheromones and biting, ants establish and maintain complex social structures, ensuring the smooth functioning of the colony.In essence, ants bite as a means of defense, foraging, and communication within their colonies. Understanding these reasons sheds light on the behavior of these remarkable creatures and emphasizes the importance of respecting their role in the ecosystem.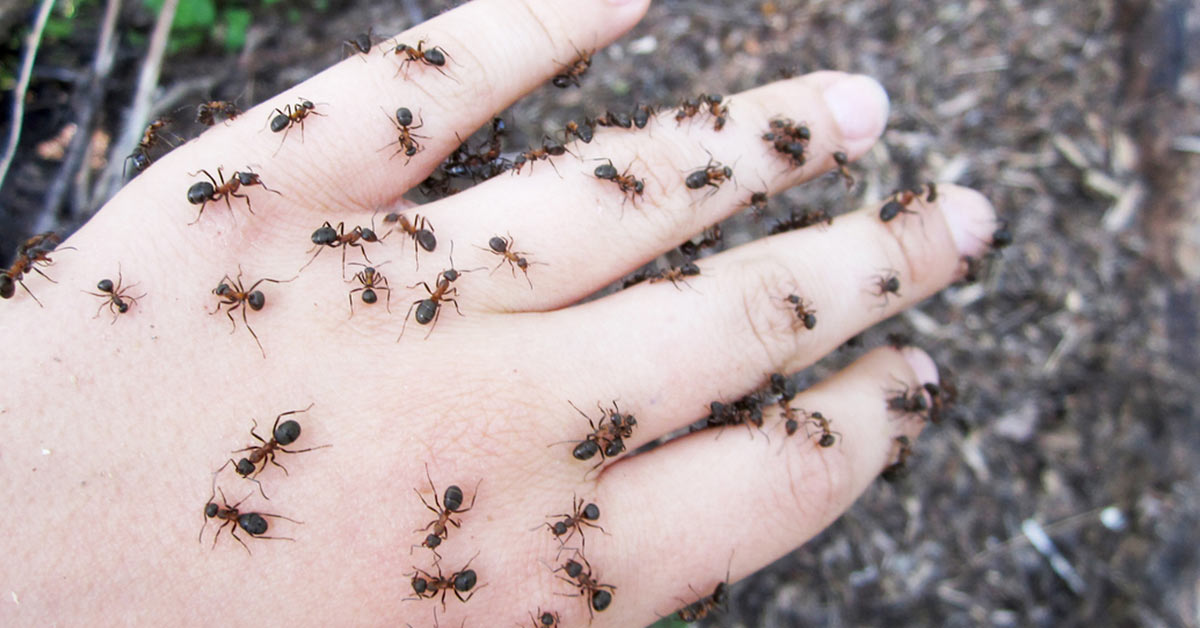
Credit: staysafe.org
Health Risks Associated With Ant Bites
Ant bites may seem insignificant, but they can pose various health risks. It is essential to understand the potential dangers associated with ant bites to protect yourself from any adverse effects. This section will discuss two primary health risks related to ant bites: allergic reactions and secondary infections.
Allergic Reactions
Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to ant bites. When an ant bites, it injects venom into the skin to incapacitate its prey or defend itself. The venom contains proteins that can trigger an allergic response in susceptible individuals. Allergic reactions can range from mild to severe, depending on the person’s sensitivity and the type of ant species involved.
Mild allergic reactions to ant bites may cause localized symptoms such as redness, itching, and swelling in the affected area. These symptoms typically subside within a few hours or days with basic home care and over-the-counter remedies. However, for individuals with severe allergies, ant bites can result in a more serious condition called anaphylaxis.
Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that requires immediate medical attention. It can manifest as difficulty breathing, chest tightness, dizziness, rapid pulse, and swelling of the face, lips, or throat. If you or someone around you experiences these symptoms after an ant bite, it is crucial to seek emergency medical care without delay. Prompt administration of epinephrine can help alleviate the potentially life-threatening effects of anaphylaxis.
Secondary Infections
In addition to allergic reactions, ant bites can also lead to secondary infections. When ants bite, they break the skin barrier, creating an entry point for bacteria. If the skin is not properly cleaned and treated, bacteria can enter the wound and cause an infection.
Secondary infections from ant bites can result in symptoms such as increased pain, redness, warmth, and pus formation at the site of the bite. If left untreated, these infections can spread and cause more severe complications. People with compromised immune systems, such as the elderly or individuals with diabetes, are particularly susceptible to developing severe infections from ant bites.
To minimize the risk of secondary infections, it is important to practice proper wound care after an ant bite. Clean the bite area with mild soap and water, apply an antiseptic cream or ointment, and cover with a clean bandage. If the infection worsens or persists, it is necessary to seek medical attention for appropriate treatment and prevention of further complications.
Overall, while ant bites may seem insignificant at first, they can have concerning health implications. Understanding the potential risks associated with ant bites helps individuals take appropriate preventive measures and seek timely medical care when necessary.
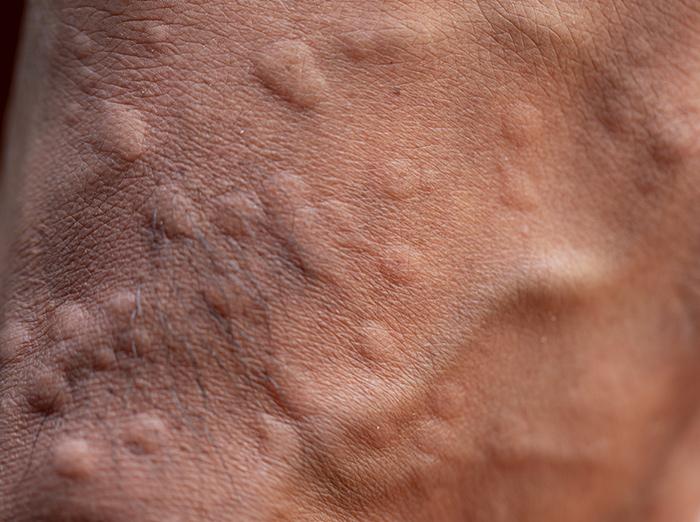
Impact Of Ant Bites On Agriculture
Damage To Crops
Ant bites can cause significant damage to crops by disrupting their growth and spreading diseases.
Control Measures
Implementing effective control measures is crucial to protect crops from ant infestations.
Credit: www.millerthekiller.com
Treatment For Ant Bites
Ant bites can be painful and itchy, causing discomfort to those affected. It is essential to know the proper treatment for ant bites to alleviate symptoms and prevent any complications.
First Aid Tips
- Wash the ant bite area with soap and warm water to prevent infection.
- Apply a cold compress or ice pack to reduce swelling and pain.
Medical Intervention
- If signs of severe allergic reaction appear, seek immediate medical attention.
- Antihistamines can be used to relieve itching and swelling from ant bites.
Preventive Measures To Avoid Ant Bites
Ant bites can be quite painful and irritating, causing redness, swelling, and itching. However, with some simple preventive measures, you can minimize the risk of getting bitten by ants. By maintaining clean surroundings and sealing potential entry points, you can effectively keep ants at bay. Let’s explore these preventive measures in more detail:
Maintaining Clean Surroundings
Maintaining cleanliness in and around your living spaces is crucial to prevent ant infestations. Here are some simple yet effective ways to maintain clean surroundings:
- Keep your kitchen clean and free of food debris by regularly wiping down countertops, sweeping the floors, and storing food properly in airtight containers.
- Regularly empty garbage cans and ensure the bins are tightly sealed to prevent ants from being attracted to the food waste.
- Maintain cleanliness in outdoor areas as well, by clearing away fallen fruits, keeping the yard free of clutter, and frequently mowing the lawn to reduce ant habitats.
Sealing Entry Points
Ants can find their way into your home through even the tiniest cracks and openings. To prevent ants from entering your living spaces, it’s important to seal potential entry points. Here’s what you can do:
- Inspect your home for any cracks or gaps in the walls, windows, doors, or foundation. Seal these openings using caulk or weather stripping.
- Ensure that window screens are intact and free of any tears or holes.
- Use door sweeps to seal the gap between the bottom of the door and the floor, preventing ants from sneaking in.
By following these preventive measures, you can minimize the risk of ant bites and keep your living spaces ant-free. Remember, a clean environment and sealed entry points are crucial in keeping ants away.
Coexistence With Ants
Ants are industrious creatures that coexist with humans in various environments. Understanding their behavior and finding natural repellents are essential for peaceful coexistence with these tiny beings.
Natural Ant Repellents
Keeping ants at bay using natural repellents is a safe and eco-friendly approach. Sprinkling cinnamon or peppermint oil at entry points can deter ants due to their aversion to strong scents. Vinegar and lemon juice are effective for wiping down surfaces to remove ant trails. Additionally, sealing food in airtight containers mitigates the risk of ant infestation.
Understanding Ant Behavior
Ants are social insects that communicate through pheromones. They leave scent trails to guide other ants to food sources, so a thorough cleaning is crucial to disrupt these trails. Understanding their foraging patterns and nesting habits also helps in preventing infestations.
Frequently Asked Questions For Why Do Ant Bite
Why Do Ants Bite Humans?
Ants bite humans as a defense mechanism or when they feel threatened. The ant’s bite injects formic acid, causing discomfort or pain. It can also occur when ants mistake human skin for food or due to territorial aggression.
How Can Ant Bites Be Treated?
To treat ant bites, wash the affected area with soap and water to prevent infection. Apply a cold compress to reduce swelling and itching. Over-the-counter antihistamines and hydrocortisone cream can help with discomfort and inflammation. Seek medical attention if experiencing severe allergic reactions.
Are All Ant Bites Painful?
Not all ant bites are painful. Some ant species deliver mild bites that may only cause minor irritation or itching. However, certain species, like fire ants, can inflict painful bites that result in swelling, redness, and discomfort. It depends on the ant species and individual reactions.
Conclusion
To sum up, ant bites can cause irritation and discomfort due to the venom they inject. While these tiny creatures may seem insignificant, they can leave a lasting impact on humans. Understanding the reasons behind their aggression, such as protecting their colonies or sensing danger, can help us prevent encounters and find effective solutions for dealing with ant bites.
Stay alert and take necessary precautions to avoid these unwelcome encounters in the future.

I’m MD Tanvir, and I bring years of expertise gained from working closely with pest control companies to the forefront. My journey in the industry has inspired me to launch Bug Battler, a platform aimed at equipping people with the know-how to combat pests autonomously. Through Bug Battler, I aim to empower individuals with practical insights to tackle pest infestations effectively.

