Bed bugs need to feed within a few days after hatching. The feeding is essential for their growth and development.
Bed bugs undergo five nymphal stages before reaching adulthood, and each stage requires a blood meal. Without feeding, they cannot progress to the next stage of development. Understanding the timeline for feeding after hatching can be crucial in managing and preventing bed bug infestations.
Knowing when the newly hatched nymphs are likely to start seeking a blood meal can help in early detection and intervention. We will delve into the feeding behavior of bed bugs after hatching and the implications for controlling their populations. We will also explore the methods for identifying and dealing with bed bug infestations at different life stages.

Credit: www.saferbrand.com
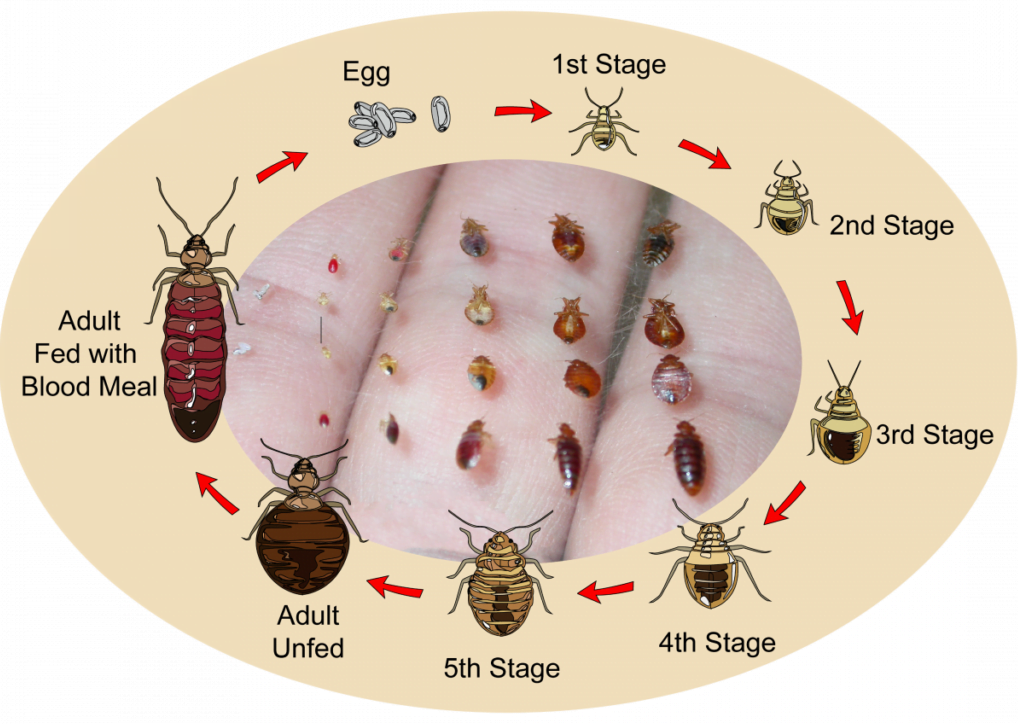
Life Cycle Of Bed Bugs
Bed bugs are small, elusive pests that can cause big problems if left unchecked. Understanding their life cycle is essential for effective control and prevention. From eggs to adults, bed bugs go through several stages of development. Let’s delve into the different stages of the bed bug life cycle to gain insights into their feeding habits and behavior.
Egg Stage
The bed bug life cycle begins with the egg stage. After mating, female bed bugs lay white, oval-shaped eggs, often in clusters, totaling to hundreds in their lifetime. These eggs are about 1mm in length, making them difficult to spot with the naked eye. They require suitable environmental conditions, including warmth and access to a blood meal, to hatch successfully.
Nymph Stage
Once the eggs hatch, they give rise to nymphs, which are immature bed bugs. Nymphs go through five molting stages, shedding their skin as they grow larger with each stage. They require a blood meal to advance to the next stage, and molting takes place between each blood meal. Nymphs are similar in appearance to adult bed bugs but are smaller and lighter in color.
Adult Stage
After completing the five nymph stages and obtaining a blood meal at each stage, the bed bugs reach the adult stage. Adult bed bugs are about the size of an apple seed, have a reddish-brown color, and a flat, oval-shaped body. Once they reach adulthood, bed bugs continue to feed on blood in order to reproduce, maintain their lifespan, and grow their population.

Credit: molekule.com
Feeding Behavior Of Bed Bugs
Bed bugs are known for being prolific feeders, and understanding their feeding behavior is crucial in controlling and preventing infestations. The frequency of feeding, as well as the signs of bed bug feeding, can provide valuable insights into their behavior and habits.
Frequency Of Feeding
Bed bugs require a blood meal to survive and reproduce. They typically feed every 5 to 10 days, but they can survive for several months without feeding under certain conditions. Female bed bugs, after mating, need to feed in order to lay eggs, which can happen within a week after their last meal. The frequency of feeding is influenced by factors such as temperature, availability of hosts, and the age of the bed bug.
Signs Of Bed Bug Feeding
Signs of bed bug feeding include itchy welts or red bumps on the skin, often arranged in a line or clustered pattern. Blood spots on bedding or nearby areas, as well as a sweet, musty odor in severe infestations, may indicate bed bug feeding. Additionally, the presence of molted exoskeletons and fecal stains on bedding and furniture can be signs of bed bug activity and feeding.
Immediate Post-hatching Feeding
Understanding how soon bed bugs require a blood meal following hatching is crucial. Immediate post-hatching feeding plays a vital role in their development and survival.
First Meal Importance
The first blood meal is essential for newly hatched bed bugs. It provides vital nutrients for growth and development.
Factors Influencing Immediate Feeding
- Temperature: Warmer temperatures prompt quicker feeding.
- Host Availability: Proximity to a host influences feeding times.
- Instinctual Urgency: Bed bugs have an innate drive to feed after hatching.

Credit: www.terminix.com
Feeding Patterns Of Newly Hatched Bed Bugs
Newly hatched bed bugs, also known as nymphs, have specific feeding patterns that differ from those of adult bed bugs. Understanding these patterns is crucial in effectively dealing with a bed bug infestation. In this section, we will explore the difference between the feeding habits of newly hatched bed bugs and adult bed bugs, as well as the duration between feedings for nymphs.
Difference From Adults
When it comes to feeding, newly hatched bed bugs have specific characteristics that set them apart from their adult counterparts. One of the key differences lies in their size. Nymphs are much smaller than adult bed bugs, measuring approximately 1.5 mm to 4.5 mm in length. This difference in size affects their feeding habits.
Unlike adult bed bugs that can find nourishment through their preference for human blood, newly hatched bed bugs have a greater willingness to feed on other sources. This includes animals or even other nymphs. This flexibility in their diet allows them to survive and grow until they reach the adult stage.
Duration Between Feedings
The feeding frequency of newly hatched bed bugs is another important aspect to consider. While adults can go without feeding for extended periods, nymphs have a more frequent need for nourishment due to their rapid growth and development.
On average, nymphs require a blood meal every 2 to 3 days to sustain their development. This short duration between feedings is crucial for their survival. Without regular access to blood, nymphs may fail to molt successfully or even die.
It’s important to note that bed bug nymphs require smaller amounts of blood compared to adult bed bugs. Nonetheless, their regular feeding schedule is necessary for their continued development and eventual maturation into adult bed bugs.
In conclusion, the feeding patterns of newly hatched bed bugs differ from those of adults. While adults have a preference for human blood, nymphs are more adaptable in their diet. Additionally, nymphs require more frequent feedings to ensure proper development and growth. Understanding these feeding habits is essential in effectively combating bed bug infestations. By targeting both nymphs and adult bed bugs, we can break their life cycle and prevent further infestations.
Health Implications
Bed bugs need to feed soon after hatching, typically within a week. This early feeding is crucial for their development and reproductive capability. Delaying their first blood meal can have detrimental effects on their health and growth, affecting their lifespan and population.
Risk Of Starvation
Without a blood meal, bed bugs face the risk of starvation. These tiny parasites have a survival strategy that relies heavily on feeding regularly. Bed bug nymphs, the immature stage of bed bugs, must feed several times to reach maturity. If they can’t find a suitable host within a certain timeframe, they can perish due to lack of sustenance.
A study conducted by researchers[1] found that bed bug nymphs can survive for only a few weeks without feeding. In comparison, adult bed bugs can survive for several months without a blood meal, which gives them a better chance of survival during periods of food scarcity. However, it is important to note that a long period of starvation diminishes the ability of bed bugs to reproduce, ultimately resulting in a decline in the infestation.
Impact On Infestation
Understanding the impact of feeding patterns on a bed bug infestation is essential for effective pest control. When bed bugs hatching from eggs cannot find a host to feed on, their population growth slows down significantly, hindering the progression of the infestation.[2] This is particularly significant for homeowners, hotels, and other establishments seeking to eradicate these pests.
The ability of bed bugs to go without feeding for a period of time can also pose challenges when attempting to eliminate them. Bed bugs can become dormant and hide in various places, such as furniture, cracks, and crevices, as they wait for a suitable feeding opportunity. This survival tactic makes it difficult to completely eradicate an infestation in a short period since the bugs can reemerge after the treatment is applied.
In conclusion, the health implications of feeding patterns for bed bugs are twofold. On one hand, the risk of starvation poses a threat to the survival and reproduction of these pests. On the other hand, the ability to withstand long periods without feeding enables the survival and persistence of an infestation. Recognizing the significance of these factors is crucial in developing effective strategies to combat bed bug infestations.
References:
- Johnson, C. G., et al. (2014). Survival and locomotion of bed bugs (Cimex lectularius L.) treated with different insecticide products. Journal of economic entomology, 107(6), 2160-2167.
- Reinhardt, K., et al. (2013). Host generalists and specialists emerging side by side: an analysis of evolutionary patterns in the cosmopolitan ectoparasite genus Cimex . Journal of evolutionary biology, 26(7), 1308-1319.
Management Strategies
Beds, crevices, cracks are common hiding spots. Tighten gaps, declutter to eliminate hiding places.
- Use mattress encasements to seal off bed bug shelters.
- Regularly vacuum and wash linens in hot water.
Seek professional help if infestation persists after DIY attempts.
- Extermination services can effectively eliminate bed bug colonies.
- Consider heat treatments to eradicate bed bugs without chemicals.
Frequently Asked Questions For How Soon After Hatching Do Bed Bugs Need To Feed?
How Soon After Hatching Do Bed Bugs Need To Feed?
Bed bugs need to feed within a few days after hatching. Once they emerge from their eggs, they start searching for blood meals to survive and grow. These tiny pests are highly skilled at finding hosts to feed on, so it’s crucial to take immediate action to prevent an infestation.
Conclusion
Considering the short time frame Bed Bugs require to feed, prompt action is crucial. Understanding their feeding habits can aid in prevention and elimination strategies. Keep your living spaces clean and vigilant to prevent infestations, safeguarding your home and family.
Stay informed and proactive against these resilient pests.
Related posts:

I’m MD Tanvir, and I bring years of expertise gained from working closely with pest control companies to the forefront. My journey in the industry has inspired me to launch Bug Battler, a platform aimed at equipping people with the know-how to combat pests autonomously. Through Bug Battler, I aim to empower individuals with practical insights to tackle pest infestations effectively.