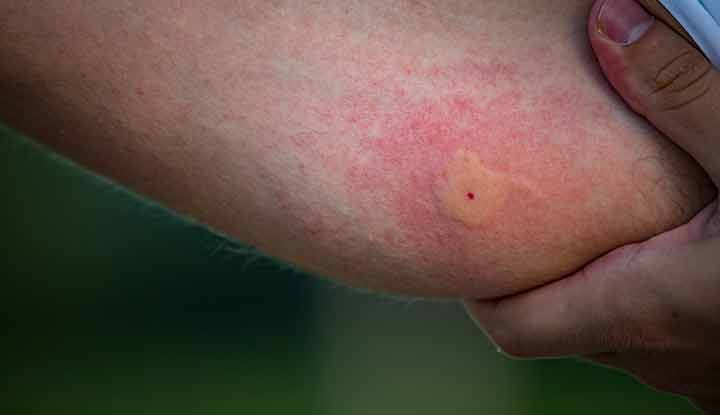
Mosquitoes can carry diseases, with the likelihood varying based on species and region. Mosquitoes are notorious for more than just their annoying bites.
They are also known carriers of various diseases that can pose serious health risks to humans. The frequency at which mosquitoes carry diseases can depend on factors such as the species of mosquito and the geographical location. Certain species, such as the Aedes aegypti mosquito, are infamous for transmitting diseases like Zika, dengue, and chikungunya.
In regions where these diseases are prevalent, the odds of mosquitoes carrying diseases are higher. Understanding the risks associated with mosquito-borne illnesses is crucial for taking preventive measures to protect oneself and others from potential health threats.

Credit: m.facebook.com
Mosquito-borne Diseases Primer
Mosquitoes can occasionally carry diseases such as West Nile virus, posing a risk to humans. It’s important to be vigilant for symptoms like body aches, fever, and headaches within two weeks of being bitten. While it’s not common, the potential for disease transmission from mosquitoes is a concern.
Common Viruses And Parasites Spread By Mosquitoes
Mosquitoes are known to transmit a variety of viruses and parasites, making them one of the most dangerous insects on the planet. Some of the most common viruses spread by mosquitoes include West Nile virus, Zika virus, and dengue fever. In addition, mosquitoes can also spread parasites such as malaria and filariasis.Geographical Distribution Of Mosquito-borne Illnesses
Mosquito-borne illnesses are found all over the world, but they are most prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions. Some of the most heavily affected areas include sub-Saharan Africa, Southeast Asia, and South America. However, cases of mosquito-borne illnesses have also been reported in the United States and other developed countries.To prevent the spread of mosquito-borne illnesses, it is important to take measures such as using insect repellent, wearing protective clothing, and eliminating standing water where mosquitoes can breed. By being aware of the risks and taking steps to protect yourself, you can greatly reduce your chances of contracting a mosquito-borne illness.
Credit: www.nps.gov
Frequency Of Disease Transmission
Mosquitoes can carry diseases such as West Nile virus. The transmission frequency varies, but bites can lead to infections.
Incidence Rates Of Mosquito-borne Diseases
Mosquitoes are not just pesky insects; they also pose a significant health risk as carriers of various diseases. The incidence rates of mosquito-borne diseases vary depending on several factors. It is crucial to understand these rates to gauge the potential risk and take appropriate preventive measures.Factors Influencing Mosquito Disease Carriage
The frequency of disease transmission by mosquitoes is influenced by several factors. Understanding these factors can help us better comprehend the risk associated with mosquito-borne diseases and implement effective prevention strategies.1. Climate and Geography: – Mosquitoes thrive in warm and humid environments, where they can breed and multiply rapidly. – Different species of mosquitoes prefer specific habitats, which may affect the prevalence of certain diseases in different regions.2. Mosquito Species: – Not all mosquito species are capable of transmitting diseases. Certain species, such as Aedes aegypti and Anopheles mosquitoes, are known vectors for diseases like Zika virus, dengue fever, and malaria. – The prevalence of these disease-carrying mosquito species may vary depending on the geographical location.3. Human Behavior and Lifestyle: – Human activities and behavior can influence the frequency of mosquito bites and subsequent disease transmission. – Factors such as outdoor activities, lack of protective measures (like mosquito nets or repellents), and living in close proximity to mosquito breeding sites can increase the risk of exposure.4. Disease Prevalence: – The prevalence of mosquito-borne diseases in a particular area can affect the likelihood of transmission. – Areas with high disease prevalence, such as regions experiencing outbreaks, may have an increased risk of mosquito-borne disease transmission.5. Public Health Measures: – The effectiveness of public health measures, such as mosquito control programs, vaccination campaigns, and public awareness campaigns, can impact the frequency of disease transmission. – Timely and targeted interventions can help reduce the mosquito population and prevent disease spread.Understanding the incidence rates of mosquito-borne diseases and the factors influencing mosquito disease carriage is crucial for implementing effective prevention strategies. By addressing these factors and taking appropriate precautions, we can minimize the risk of mosquito-borne diseases and protect our health.Understanding Mosquito Feeding Behavior
Understanding mosquito feeding behavior is crucial to understanding how often mosquitoes carry diseases. Once a mosquito feeds on an infected host, it can transmit the disease to its next victim. Mosquitoes can carry a variety of diseases, such as West Nile virus and malaria, so it’s important to take preventative measures to avoid getting bitten.
Life Cycle Of Blood-feeding Mosquitoes
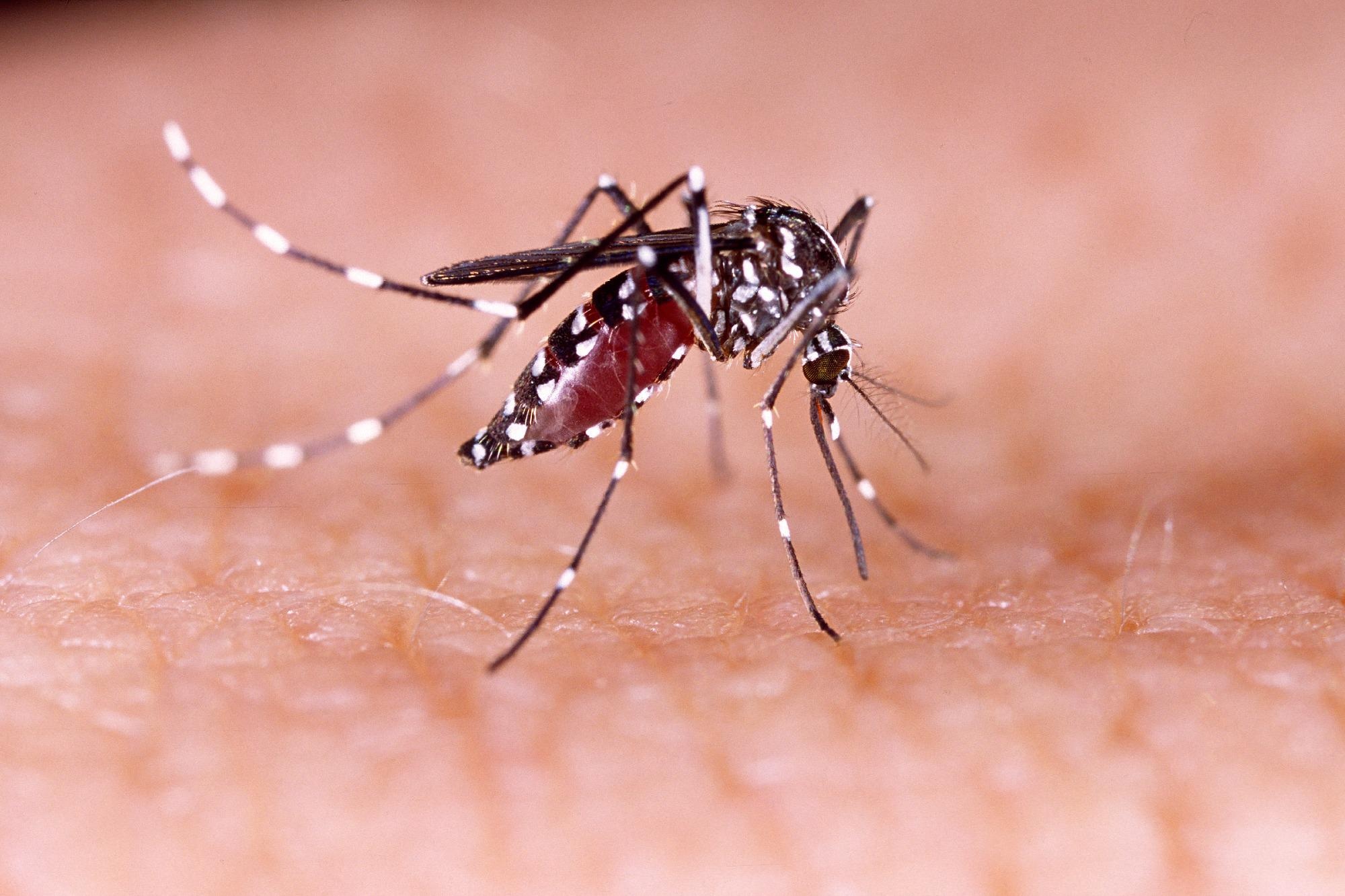
Mosquitoes, those tiny buzzing pests, have a fascinating life cycle that revolves around their need for blood. Understanding their life cycle can help us comprehend their potential for carrying diseases. Let’s take a closer look at the life cycle of blood-feeding mosquitoes.Mosquitoes go through four distinct stages in their life cycle: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Female mosquitoes are the ones responsible for blood-feeding, as they require the protein found in blood to develop their eggs. After mating, a female mosquito seeks out a suitable host to feed on. Once she finds a host, she lands on their skin and begins to feed by inserting her proboscis into the skin to access the blood vessels beneath.How Many Bites Can One Mosquito Inflict?
Have you ever wondered just how many times a mosquito can bite you? Well, mosquitoes are persistent creatures when it comes to feeding. Unlike some insects that bite once and fly away, mosquitoes are capable of multiple bites in a single feeding session.Once a female mosquito lands on a host, she begins probing the skin to find a suitable blood vessel. With each successful probe, she injects her saliva, which contains anticoagulants to prevent blood clotting. This saliva can cause itchiness and irritation to the host. The mosquito then feeds on the blood until she is full, which usually takes only a few minutes. However, if she is interrupted or unable to find a suitable blood vessel, she may move on to another location on the host’s body and attempt to bite again.It’s important to note that not all mosquito bites result in disease transmission. Mosquitoes are the primary vectors for diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, Zika virus, and West Nile virus. However, the likelihood of a mosquito carrying a disease-causing pathogen depends on various factors, including the prevalence of the disease in the mosquito population and the geographical location.In conclusion, understanding mosquito feeding behavior is crucial when considering the potential transmission of diseases. By knowing their life cycle and the number of bites they can inflict, we can better protect ourselves from mosquito-borne illnesses. Taking preventive measures, such as using insect repellents, wearing protective clothing, and eliminating breeding sites, can help reduce the risk of mosquito bites and the diseases they may carry. Stay informed and stay safe!Disease Transmission Mechanics
Mosquitoes are known to occasionally transmit diseases, such as West Nile virus, to humans. The likelihood of contracting a disease from a mosquito bite depends on various factors, including the prevalence of the disease in the area and the behavior of the mosquito population.
It is important to take precautions to avoid mosquito bites and monitor for any symptoms of illness after being bitten.
Disease Transmission MechanicsMosquitoes are notorious for transmitting a wide range of diseases, including malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus, among others. But how exactly do mosquitoes transmit these diseases? The process from bite to infection can be broken down into several steps.The Process from Bite to InfectionWhen a mosquito bites a human, it pierces the skin and injects its saliva, which contains anticoagulants to prevent blood from clotting. If the mosquito is carrying a virus or parasite, it can also be transmitted into the human’s bloodstream through the mosquito’s saliva.Once the virus enters the human’s system, it begins to replicate and spread throughout the body. The immune system responds by producing antibodies to fight off the infection, but this process can take time, leaving the individual vulnerable to the disease.Time Frame for Disease TransmissionThe time it takes for a mosquito to transmit a disease can vary depending on several factors, including the type of virus or parasite, the individual’s immune system, and the mosquito’s feeding habits. In some cases, the virus can be transmitted within minutes of the mosquito bite, while in others, it may take several days or weeks.For example, the Zika virus can be transmitted within minutes of a mosquito bite, while malaria parasites typically take several days to develop in the mosquito’s body before being transmitted to a human.ConclusionUnderstanding the disease transmission mechanics of mosquitoes is crucial in preventing the spread of mosquito-borne diseases. By taking preventive measures, such as using mosquito repellents, wearing protective clothing, and eliminating standing water around homes, individuals can reduce their risk of infection and protect themselves and their communities from these deadly diseases.Assessing The Risk Of Infection
Mosquitoes can carry diseases such as West Nile virus and Zika virus. Knowing the risk of infection after a mosquito bite is crucial for timely medical attention.
Symptoms To Watch After Mosquito Bites
- Fever
- Body aches
- Headaches
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
When To Seek Medical Attention
If you experience symptoms like fever, body aches, or nausea within two weeks of a mosquito bite, consult your doctor. Early detection is key in preventing complications from mosquito-borne diseases.
Protective Measures Against Mosquitoes
Mosquitoes are known carriers of various diseases, including West Nile virus, Zika virus, and malaria. Understanding protective measures against mosquitoes is crucial for preventing the spread of these diseases.
Personal Preventive Practices
Implementing personal preventive practices can significantly reduce the risk of mosquito-borne diseases. Here are some effective measures:
- Apply insect repellent containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus.
- Wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants to minimize exposed skin.
- Install screens on windows and doors to prevent mosquitoes from entering indoor spaces.
- Use mosquito nets while sleeping, especially in areas with high mosquito activity.
- Eliminate standing water around the home to remove mosquito breeding grounds.
Community-level Control Strategies
Community-level control strategies play a vital role in managing mosquito populations and reducing disease transmission. Some effective strategies include:
- Implementing mosquito surveillance and monitoring programs to track population densities and disease prevalence.
- Conducting larviciding and adulticiding activities in areas with high mosquito populations to reduce their numbers.
- Engaging in community education and outreach programs to raise awareness about mosquito-borne diseases and prevention methods.
- Coordinating with local authorities to implement integrated pest management practices for long-term mosquito control.
Impact Of Climate And Environment
Mosquitoes can carry diseases such as West Nile virus, dengue, Zika, and malaria. The frequency of disease transmission depends on various factors, including the prevalence of infected mosquitoes, the geographical location, and the health of the human population. Taking precautionary measures like using mosquito repellent and eliminating breeding sites can help reduce the risk of mosquito-borne diseases.
Effects Of Weather On Mosquito Populations
Weather influences mosquito populations, affecting their breeding and activity levels.
Mosquito Habitats And Disease Risks
Mosquito habitats, such as standing water, increase the risk of disease transmission.
Global And Public Health Perspectives
When considering global and public health perspectives, it is crucial to understand the impact of mosquito-borne diseases worldwide.
Controlling Mosquito-borne Diseases Worldwide
Mosquito-borne diseases pose a significant threat to public health globally.
Research And Innovations In Mosquito Disease Prevention
Continuous research and innovative strategies are essential in preventing the spread of mosquito-borne diseases.
Credit: www.news-medical.net
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Odds Of Getting A Disease From A Mosquito?
The odds of getting a disease from a mosquito bite vary based on the specific type of mosquito and the disease it may be carrying. Mosquitoes can transmit diseases such as West Nile virus, dengue fever, and malaria. It is important to take preventative measures such as using mosquito repellent and wearing protective clothing when in areas with high mosquito activity.
When Should You Worry About A Mosquito Bite?
You should worry about a mosquito bite if you experience symptoms like body aches, diarrhea, fever, headaches, or nausea within two weeks of the bite. Contact your doctor if you suspect a mosquito-borne disease.
How Long Does A Mosquito Have To Bite To Transmit Disease?
Mosquitoes need 8 to 12 days to transmit diseases after biting an infected person.
Conclusion
Mosquitoes can carry diseases such as West Nile virus and malaria. It’s important to take precautions to avoid mosquito bites and reduce the risk of infection. Understanding the potential for disease transmission can help individuals and communities take proactive measures to stay safe and healthy.
Related posts:

I’m MD Tanvir, and I bring years of expertise gained from working closely with pest control companies to the forefront. My journey in the industry has inspired me to launch Bug Battler, a platform aimed at equipping people with the know-how to combat pests autonomously. Through Bug Battler, I aim to empower individuals with practical insights to tackle pest infestations effectively.