Bed bugs typically hatch within 6 to 10 days after the eggs are laid. This timeframe may vary based on temperature and environmental conditions.
Dealing with a bed bug infestation can be a stressful situation for homeowners. Understanding the life cycle of these pests is crucial in effectively combating them. From egg to nymph to adult, bed bugs go through several stages of development, with each phase bringing its own challenges.
Knowing when and how bed bugs hatch can help in devising a comprehensive strategy to eradicate them from your living space. We will delve into the timeline of bed bug hatchings and provide insights on how to deal with these persistent insects.
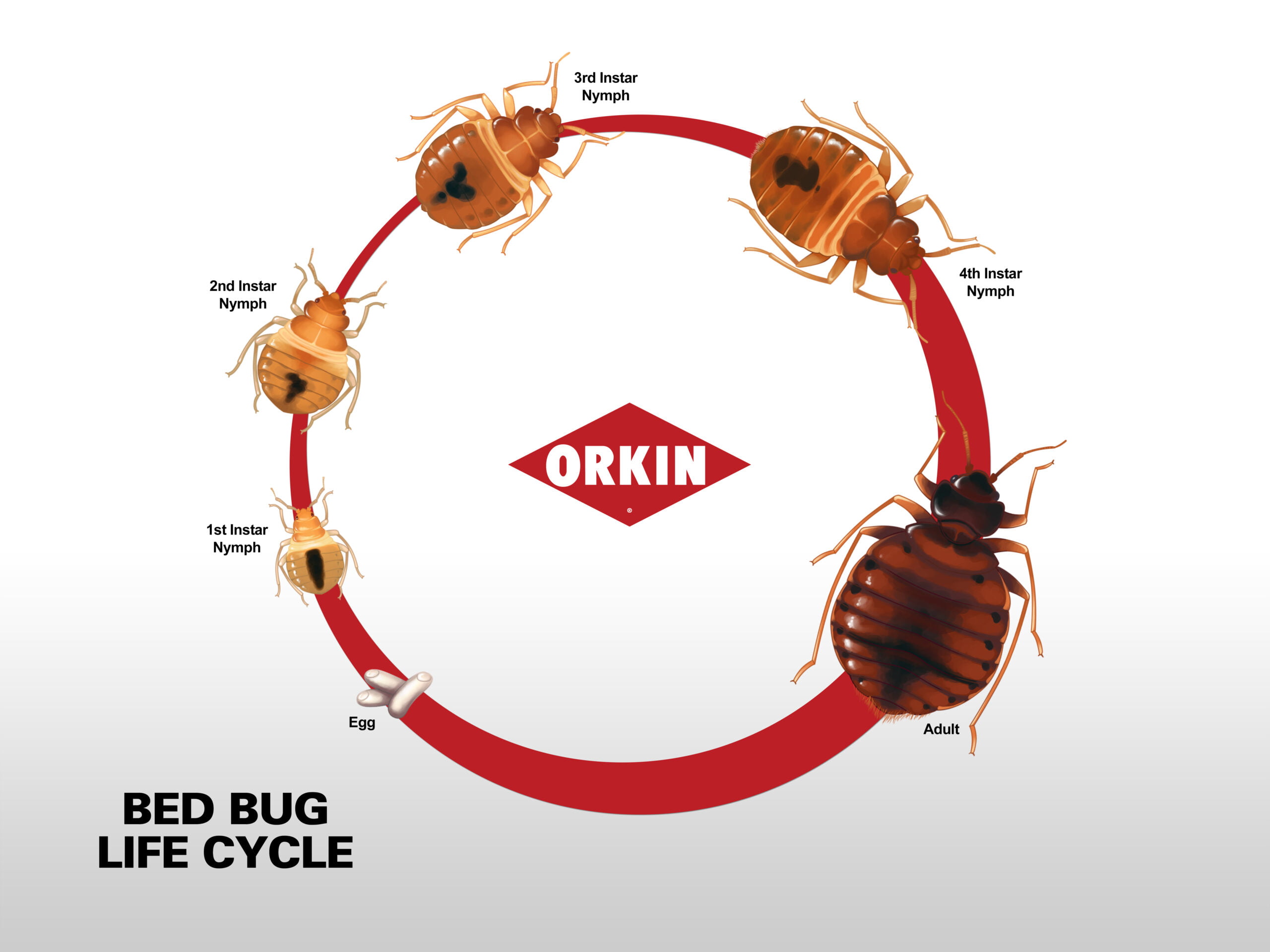
Life Cycle Of Bed Bugs
The life cycle of bed bugs consists of several stages from eggs to nymphs and, finally, adults. Understanding this cycle is crucial in dealing with infestations effectively.
Bed bug eggs are tiny, usually a milky white color, and barely visible to the naked eye. They are laid in clusters and typically hatch within about 6 to 10 days.
Once hatched, bed bug nymphs resemble smaller versions of adult bed bugs. They go through five molting stages before reaching adulthood, with each stage requiring a blood meal to progress.
Adult bed bugs are reddish-brown, flat, and oval-shaped. They can live up to a year or more under favorable conditions. Mating occurs after each blood meal, leading to the continuation of the reproductive cycle.
Credit: www.custombedbug.com
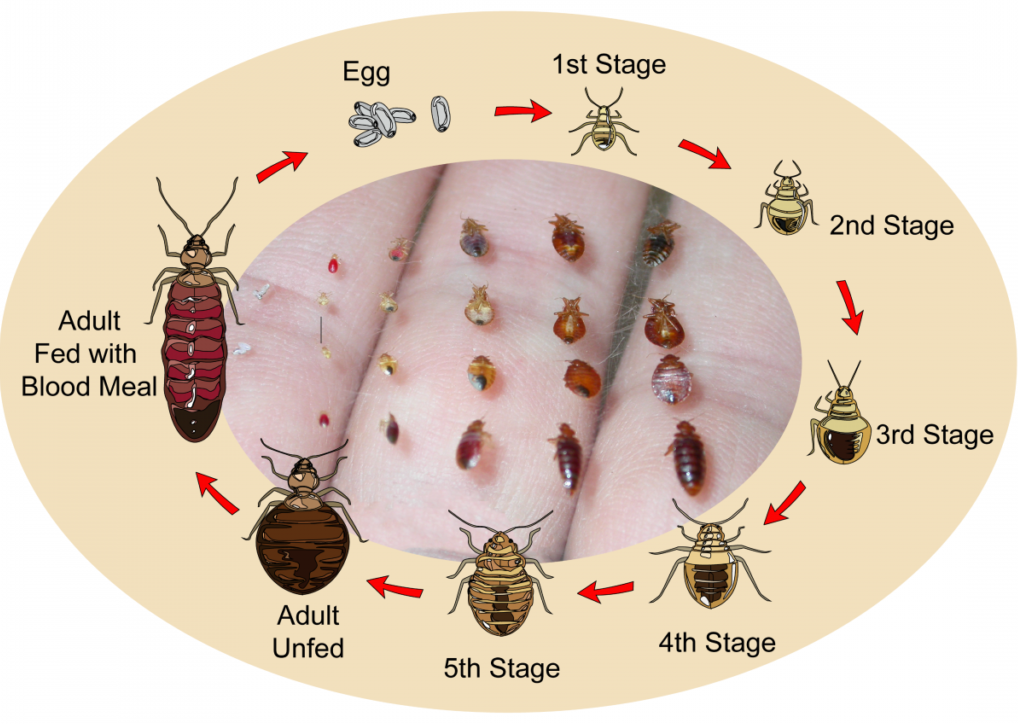
Eggs
Eggs are laid by bed bugs and typically hatch within 6 to 10 days. The hatching time can vary based on temperature and humidity levels.
Hatching Process
Incubation Period
Bed bugs lay their eggs in hidden places you may not even notice. The eggs are tiny, white, and sticky, making them adhere to surfaces.
Bed bug eggs are about the size of a pinhead and are often laid in clusters. The female bed bug can lay hundreds of eggs during her lifetime. The eggs are sticky and adhere to surfaces, making them hard to remove.
After a bed bug egg is laid, it goes through a process of incubation before hatching into a nymph.
Hatching Process
- Bed bug eggs hatch in approximately 6 to 10 days under normal room conditions.
- Once hatched, the nymphs emerge and start searching for a blood meal.
- Nymphs molt and grow through five instar stages before reaching adulthood.
Incubation Period
| Temperature | Incubation Period |
|---|---|
| 70°F | 6-10 days |
| 80°F | 5-9 days |
| 90°F | 4-8 days |
Nymphs
One of the most crucial stages in the life cycle of a bed bug is the nymph stage. Nymphs are the immature bed bugs that hatch from eggs. Understanding the development stages and feeding habits of these nymphs is essential to effectively dealing with a bed bug infestation.
Development Stages
Bed bugs undergo five nymphal stages, commonly known as instars, before reaching adulthood. Each nymphal stage is marked by a molt, during which the nymph sheds its exoskeleton and grows to the next stage. The time it takes for bed bug nymphs to complete each stage varies depending on various factors such as temperature, availability of food, and environmental conditions.
| Development Stage | Time Duration |
|---|---|
| Nymph 1 | 5-10 days |
| Nymph 2 | 4-9 days |
| Nymph 3 | 4-8 days |
| Nymph 4 | 4-8 days |
| Nymph 5 | 5-10 days |
Feeding Habits
Upon hatching, nymphs are eager to feed on blood as their primary source of nourishment. Bed bug nymphs require a blood meal to molt and grow to the next stage. Although nymphs can survive for short periods without feeding, they must eventually obtain blood to progress in their development.
During the nymphal stages, bed bugs feed approximately once every few days, as they need time to digest the blood meal and molt. Unlike adults, nymphs do not possess wings and cannot fly. This means that they typically feed in close proximity to their harborages, often found near sleeping areas.
When a bed bug nymph locates a suitable host, it pierces the skin with its mouthparts and injects saliva containing an anesthetic and anticoagulant to facilitate feeding. The nymph then feeds for a few minutes until it becomes engorged with blood, causing its body to swell and turn reddish in color. After feeding, nymphs retreat to their harborage to digest the blood meal and molt to the next stage.
It is important to note that bed bug nymphs molt five times before reaching adulthood. Therefore, if you are dealing with a bed bug infestation, it is essential to eliminate not only the adult bugs but also their nymphs to prevent further infestation.
Adults
After feeding, female bed bugs lay tiny eggs that hatch in about 6 to 10 days. These newly hatched bed bugs need a blood meal to grow and molt into adults. The entire process from egg to adult takes about 4 to 9 weeks.
Reproduction
Bed bugs are known for their prolific reproductive capacity, with adult females capable of laying one to five eggs per day. After mating, the female typically lays her eggs within a week, and these eggs take about six to ten days to hatch.
Longevity
Adult bed bugs can live for several months without a blood meal. Under favorable conditions, they can survive up to a year or more, making them resilient pests that are challenging to eradicate.
Factors Affecting Hatching Time
Bed bug hatching time is influenced by temperature and environmental conditions. Typically, it takes 4-12 days for bed bug eggs to hatch. Warmer temperatures accelerate the hatching process, while cooler conditions slow it down. Factors such as humidity and access to a blood meal also affect the hatching time.
Factors Affecting Hatching TimeTemperatureThe temperature plays a crucial role in the hatching time of bed bug eggs. Warmer temperatures generally result in quicker hatching. Bed bug eggs usually hatch within 6 to 10 days at room temperature (around 70-80°F).Availability of FoodThe availability of food sources also impacts the hatching time of bed bugs. If food is readily available, eggs are more likely to hatch sooner. Conversely, if bed bugs are starved, the hatching process may be delayed.Understanding these factors can help predict and manage bed bug infestations efficiently.
Credit: www.purcorpest.com
Detecting Bed Bug Infestations
Finding out if you have a bed bug infestation is crucial to prevent an infestation from spreading. Effective management of bed bug problems begins with early detection. Knowing the signs to look for and the methods to inspect your living spaces will help you identify and address a bed bug infestation promptly. In this section, we will explore how to detect bed bug infestations.
Signs Of Bed Bugs
Being able to recognize the signs of bed bugs is the first step in detecting an infestation. Here are some key indicators to look out for:
- Blood stains or rust-colored spots on your sheets or mattress caused by bed bug bites.
- Small dark spots (bed bug excrement) on your bedding or furniture.
- Eggshells or shed skins in the areas where bed bugs hide.
- A sweet musty odor that is often associated with bed bug infestations.
Inspection Methods
To confirm the presence of bed bugs, thorough inspections using different methods can be carried out. Here are some reliable inspection methods:
- Visual Inspection: Examine your mattress, box springs, headboard, and any nearby furniture visually for live bed bugs or their signs.
- Use a Flashlight: Bed bugs are nocturnal creatures, so using a flashlight during your inspection can help you spot them in dark corners, crevices, or cracks.
- Bed Bug Monitors: These specialized devices can be placed under your mattress or near potential harborage areas to trap and detect bed bugs.
- Clutter Removal: Reducing clutter around your living spaces not only eliminates potential hiding spots for bed bugs but also allows for easier visual inspections.
Preventing And Eliminating Bed Bugs
Regularly inspect your living space for bed bugs through visual checks and bed bug detectors.
Professional extermination may be required for severe infestations. Wash and heat dry bedding and clothing.

Credit: www.saferbrand.com
Frequently Asked Questions On How Long Does It Take For Bed Bugs To Hatch After?
How Long Does It Take For Bed Bugs To Hatch After Mating?
Bed bugs can hatch within 6 to 17 days after mating, depending on environmental conditions like temperature and humidity.
What Are The Factors That Affect Bed Bug Hatching Time?
The hatching time of bed bugs is influenced by temperature, humidity, and the availability of a suitable host.
Can Bed Bugs Lay Eggs Without Mating?
Yes, female bed bugs can lay viable eggs without mating, a process known as parthenogenesis. However, mating can increase the fertility rate and egg production.
What Is The Fastest Way To Get Rid Of Bed Bug Eggs?
To eliminate bed bug eggs, use a combination of vacuuming, steam cleaning, and targeted insecticide application, while maintaining hygiene and eliminating clutter.
Conclusion
To conclude, it is essential to understand the timeline of bed bug hatching. From egg to nymph, it generally takes around 6-10 days, but this can vary depending on various factors. By regularly monitoring and taking prompt action, you can prevent a bed bug infestation from escalating.
Remember to consult a professional for effective treatment and ensure a peaceful, bug-free environment. Stay informed to keep your home bed bug-free!
Related posts:

I’m MD Tanvir, and I bring years of expertise gained from working closely with pest control companies to the forefront. My journey in the industry has inspired me to launch Bug Battler, a platform aimed at equipping people with the know-how to combat pests autonomously. Through Bug Battler, I aim to empower individuals with practical insights to tackle pest infestations effectively.