Cockroaches reproduce through sexual reproduction, with males attracting females using pheromones and depositing sperm during mating. These insects are oviparous, meaning their young grow in eggs outside the mother’s body.
Cockroach eggs are typically laid in safe, damp places close to a food source. Once the eggs hatch, nymphs emerge and go through several molts before reaching adulthood. This process allows cockroaches to multiply quickly and adapt to various environments.
Understanding the reproductive behavior of cockroaches is crucial in controlling their population and preventing infestations. By implementing effective pest control measures, it is possible to manage and eliminate these resilient pests from homes and other spaces.
Cockroach Reproduction Basics
Cockroach reproduction involves mating, with males attracting females through wing flapping. Once the male deposits sperm, the female lays eggs in a safe, damp location, typically close to a food source but far from human reach.
Cockroach Anatomy
Understanding the anatomy of cockroaches is crucial to grasp how they reproduce. Cockroaches are brown or black-colored animals that belong to the phylum Arthropoda. They are dioecious organisms, meaning there are separate male and female individuals. Cockroaches are nocturnal omnivores, scavenging for food during the night. With their flattened bodies and fast-moving legs, they can easily navigate through tight spaces.
Cockroach Mating Behaviors
Mating in cockroaches is an intriguing process. Attracted males approach females and flap their wings to denote interest. Reproduction commences when a male cockroach backs into a female cockroach, depositing sperm. This behavior is known as “traumatic insemination” as it involves the male piercing the female’s abdomen to transfer sperm. Although this process may seem aggressive, it is a natural part of their reproductive cycle.
Cockroach Eggs And Oothecae
Cockroaches lay their eggs in safe, damp, and hidden places. Female cockroaches produce oothecae, which are protective egg cases. These oothecae contain multiple eggs and are attached to various surfaces like cupboards or cardboard near a food source. This ensures the survival and protection of the eggs until they hatch. The eggs develop outside of the mother’s body, and most cockroaches are oviparous, meaning their young grow in eggs.
Overall, understanding the basics of cockroach reproduction is essential for effective pest control. By knowing their anatomy, mating behaviors, and egg-laying habits, it becomes easier to implement preventive measures and combat infestations.
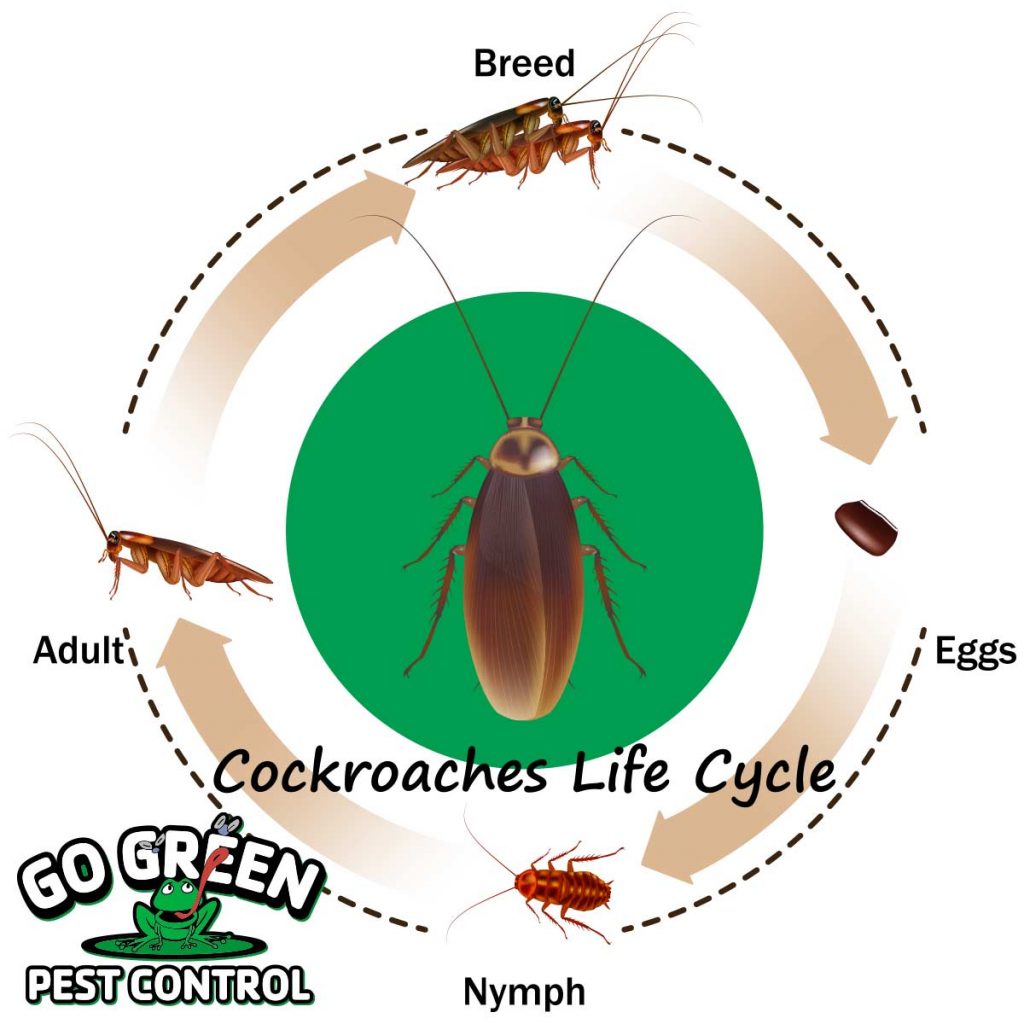
Cockroach Life Cycle
Cockroaches reproduce through a process called mating, where attracted males approach females and deposit sperm. The female cockroach then lays eggs in safe and hidden areas, ensuring the survival of the next generation.
Egg Stage
Cockroaches have a fascinating life cycle that begins with the egg stage. Female cockroaches lay their eggs in safe and hidden places that are often damp. These places could include cracks in walls, behind appliances, or in dark corners of the house. The eggs are enclosed in a protective casing called an ootheca. Each ootheca can contain multiple eggs, depending on the species of cockroach.
Nymph Stage
Once the eggs hatch, nymphs emerge. Nymphs are miniature versions of adult cockroaches but lack wings. During the nymph stage, they undergo a series of molts, shedding their exoskeletons as they grow. Each molt brings them closer to adulthood and the development of wings. Nymphs are active and agile, often exploring their surroundings in search of food and water.
Adult Stage
After several molts, nymphs reach the adult stage. Adult cockroaches have fully developed wings and are capable of reproducing. They continue to search for food and water, often venturing out at night when they are most active. The lifespan of an adult cockroach can vary depending on the species, but generally, they can live for several months to a year.
In conclusion, the cockroach life cycle consists of three main stages: the egg stage, nymph stage, and adult stage. Understanding this life cycle is crucial for effective pest control and prevention. By disrupting their reproductive cycle, it is possible to reduce the population of cockroaches in your home and minimize the risk of infestation.
Factors Affecting Cockroach Reproduction
Cockroaches reproduce through sexual reproduction, where the male deposits sperm into the female. Factors affecting cockroach reproduction include temperature, humidity, food availability, and the presence of predators or competitors. Roaches reproduce quickly, with some species capable of producing hundreds of offspring in a short period.
Factors Affecting Cockroach Reproduction: Cockroaches are known for their ability to reproduce at a rapid rate. However, several factors can influence the reproductive behavior of cockroaches. The environmental, social, and genetic factors play a crucial role in cockroach reproduction. Let’s take a closer look at each of these factors. HTML H3 Heading – Environmental Factors: The environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and food availability can significantly influence the reproductive behavior of cockroaches. Cockroaches prefer warm and humid environments, and they reproduce more rapidly in such conditions. The availability of food also plays a crucial role in cockroach reproduction. A steady supply of food can increase the reproductive rate of cockroaches. HTML H3 Heading – Social Factors: Cockroaches are social insects, and their reproductive behavior is influenced by the presence of other cockroaches. The presence of male cockroaches can stimulate the reproductive behavior of female cockroaches. In addition, the density of cockroach populations can also affect their reproductive behavior. High-density populations can lead to increased competition for resources, which can result in increased reproductive behavior. HTML H3 Heading – Genetic Factors: Genetic factors also play a crucial role in cockroach reproduction. Cockroaches have a unique genetic makeup that determines their reproductive behavior. Some species of cockroaches have evolved to reproduce more rapidly than others. In addition, genetic diversity can also influence the reproductive behavior of cockroaches. A lack of genetic diversity can lead to inbreeding, which can result in reduced reproductive success. In conclusion, several factors can influence the reproductive behavior of cockroaches. Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and food availability can significantly affect cockroach reproduction. Social factors such as the presence of other cockroaches and the density of cockroach populations can also influence their reproductive behavior. Genetic factors such as genetic makeup and diversity can also play a crucial role in cockroach reproduction.

Credit: www.terminix.com
Cockroach Reproduction Strategies
Cockroaches reproduce through a process called parthenogenesis, allowing females to lay eggs without male participation. They produce oothecae, protective cases containing multiple eggs, which are then deposited in safe, hidden, and damp areas. Mating occurs when males approach females and deposit sperm, initiating the reproductive cycle.
Cockroaches are known for their ability to reproduce quickly and efficiently, making them a common pest problem in many households. Cockroaches have three main reproduction strategies: sexual reproduction, asexual reproduction, and parthenogenesis. Understanding these strategies can help you identify and control cockroach infestations in your home.
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction is the most common method of reproduction for cockroaches. Male cockroaches use pheromones to attract females for mating. Once the female accepts the male’s advances, the male deposits his sperm into the female’s reproductive system. The female then lays an egg case, which contains multiple eggs. The eggs hatch into nymphs, which develop into adult cockroaches.
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction, also known as parthenogenesis, is a rare method of reproduction for cockroaches. Female cockroaches are capable of producing offspring without mating with a male. In this process, the female produces an egg that develops into a new cockroach without fertilization from a male. However, the offspring produced through asexual reproduction are genetically identical to the mother and lack genetic diversity.
Parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis is a unique form of asexual reproduction that occurs in some species of cockroaches. In this process, the female produces an egg that develops into a new cockroach without fertilization from a male. However, unlike asexual reproduction, the offspring produced through parthenogenesis are not genetically identical to the mother. Instead, they are a mix of the mother’s genetic material and a set of chromosomes that the mother receives from an unknown source. In conclusion, understanding the reproductive strategies of cockroaches can help you identify and control infestations in your home. By taking preventative measures such as keeping your home clean and sealing entry points, you can reduce the likelihood of cockroaches reproducing and multiplying.
Cockroach Infestations
Cockroach infestations can be a major nuisance and pose serious health risks. Understanding the signs of a cockroach infestation, prevention and control methods, as well as professional cockroach extermination, is crucial in dealing with these resilient pests.
Signs Of A Cockroach Infestation
Identifying the presence of cockroaches in your home is essential for prompt action. The signs of a cockroach infestation include:
- Foul Odor: A musty, oily smell that indicates the presence of cockroaches.
- Droppings: Tiny, black droppings resembling coffee grounds, often found in kitchen cabinets or drawers.
- Egg Casings: Small, brown casings left behind by hatched cockroach eggs.
- Visible Roaches: Spotting live cockroaches, especially in the kitchen or bathroom, is a clear sign of infestation.
Prevention And Control Methods
To prevent and control cockroach infestations, it’s important to:
- Maintain Cleanliness: Regularly clean and sanitize all areas of the home, especially the kitchen and bathrooms.
- Seal Entry Points: Seal cracks, crevices, and gaps to prevent cockroaches from entering the home.
- Remove Food Sources: Store food in airtight containers and clean up spills promptly to eliminate food sources for cockroaches.
- Use Baits and Traps: Place cockroach baits and traps in strategic locations to capture and eliminate the pests.
Professional Cockroach Extermination
Seeking professional cockroach extermination services is often the most effective way to eradicate a persistent infestation. Professional exterminators can employ targeted treatments and ongoing monitoring to ensure complete elimination of cockroaches from your home.
Credit: www.gogreenpestcontrol.com
Cockroach Reproduction Faqs
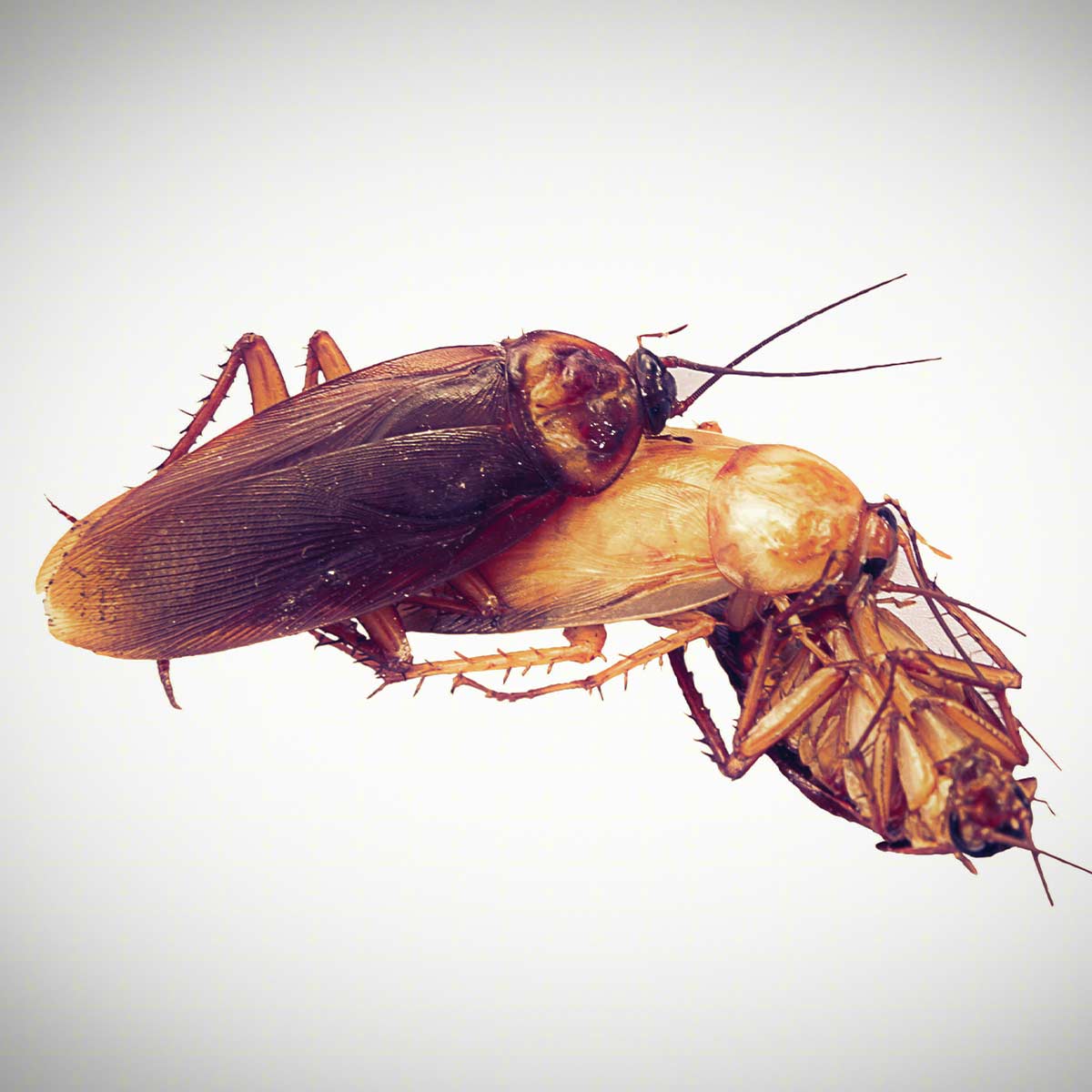
Cockroaches reproduce quickly and efficiently through sexual reproduction, with males depositing sperm inside females. After mating, the female carries the eggs in an ootheca until they hatch. This process allows cockroaches to multiply rapidly, making them a challenging pest to control.
How Fast Do Cockroaches Reproduce?
Cockroaches are known for their rapid reproduction rate. A single female cockroach can produce multiple batches of eggs, with each batch containing dozens of offspring. The gestation period for cockroach eggs is relatively short, typically ranging from 40 to 60 days, depending on the species.
Where Do Cockroaches Lay Eggs?
Cockroaches prefer to lay their eggs in dark, secluded areas that provide moisture and protection. Common egg-laying sites include cracks and crevices in walls, under appliances, and in cluttered areas. The egg cases, known as oothecae, are often glued to surfaces to safeguard them from predators and environmental factors.
Do Cockroaches Reproduce Asexually?
Scientists have observed that female cockroaches can engage in parthenogenesis, a form of asexual reproduction. This process allows female cockroaches to produce eggs without the need for male fertilization. The resulting offspring are genetically identical to the mother and are all-female. However, sexual reproduction is the primary mode of reproduction for most cockroach species.

Credit: www.gogreenpestcontrol.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Quickly Do Cockroaches Multiply?
Cockroaches multiply quickly. Female cockroaches lay eggs every few weeks, with each egg sac containing up to 50 eggs. Depending on the species, it can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months for the eggs to hatch and develop into adult cockroaches capable of reproducing.
Do Roaches Reproduce Asexually?
Yes, some species of roaches can reproduce asexually through a process called parthenogenesis, where females produce eggs without male participation. However, the offspring produced through parthenogenesis are all-female.
Where Do Cockroaches Lay Eggs?
Cockroaches lay their eggs in damp or hidden places close to food but away from human reach. Female cockroaches glue their eggs to hard surfaces like cupboards or cardboard near food sources.
Conclusion
To sum up, cockroaches are notorious for their reproductive abilities, with some species capable of producing hundreds of offspring in a single year. They use pheromones to attract mates and reproduce through sexual reproduction. However, some species can also reproduce through parthenogenesis, where females can produce eggs without male participation.
To prevent a cockroach infestation, it is essential to maintain cleanliness and address any moisture issues in the home. With this knowledge, you can take the necessary steps to keep these pesky pests at bay.
Related posts:

I’m MD Tanvir, and I bring years of expertise gained from working closely with pest control companies to the forefront. My journey in the industry has inspired me to launch Bug Battler, a platform aimed at equipping people with the know-how to combat pests autonomously. Through Bug Battler, I aim to empower individuals with practical insights to tackle pest infestations effectively.

