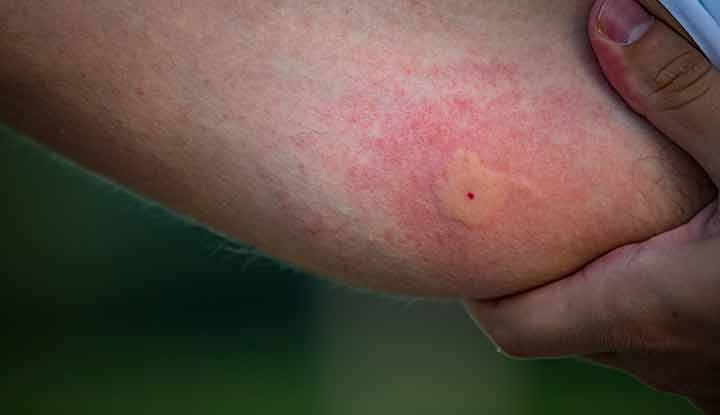
Mosquitoes can carry diseases, but not all mosquitoes are disease carriers. The likelihood of a mosquito carrying a disease varies based on the species and region.
In areas where diseases like malaria, dengue, West Nile virus, chikungunya, yellow fever, and Zika are prevalent, the chances of mosquitoes transmitting diseases are higher. Taking precautions such as using insect repellent and wearing protective clothing can help reduce the risk of mosquito-borne illnesses.
Understanding the transmission patterns of these diseases can also aid in implementing effective prevention strategies. By being informed and proactive, individuals can better protect themselves from the potential health risks associated with mosquito bites.
The Prevalence Of Disease-carrying Mosquitoes
Mosquitoes are known to carry various diseases, including malaria, dengue, West Nile virus, chikungunya, yellow fever, and Zika. Once a mosquito bites a person infected with a disease, it can spread the virus to other people while feeding. The best way to avoid infection is to prevent mosquito bites.
Mosquito-borne Diseases: A Global Concern
Mosquitoes pose a significant threat as carriers of deadly diseases around the world. These diseases can have severe consequences for human health and well-being. Preventing mosquito-borne illnesses is crucial to safeguarding communities.Statistics On Mosquito Disease Transmission
– Mosquitoes are responsible for transmitting a variety of diseases, including malaria, dengue, West Nile virus, chikungunya, yellow fever, and Zika. – Each year, millions of people are affected by mosquito-borne illnesses, leading to significant morbidity and mortality rates. – The prevalence of disease-carrying mosquitoes varies by region, with some areas experiencing higher rates of infection than others. – The World Health Organization estimates that mosquitoes infect over 700 million people annually with diseases like malaria and dengue. – Effective mosquito control measures are essential to reduce the spread of these diseases and protect public health.Identifying High-risk Areas
Mosquitoes are not just pesky insects; they can also pose a significant health risk due to their ability to carry and transmit diseases. Identifying high-risk areas for mosquito-borne diseases is crucial for implementing targeted prevention and control measures.
Geographical Hotspots For Mosquito Diseases
Geographical locations play a crucial role in determining the prevalence of mosquito-borne diseases. Certain regions are considered hotspots due to favorable environmental conditions that support the breeding and proliferation of disease-carrying mosquitoes. These hotspots are often characterized by warm and humid climates, which create ideal breeding grounds for mosquitoes.
Environmental Factors Affecting Mosquito Populations
Various environmental factors can significantly impact mosquito populations and the spread of diseases. Factors such as stagnant water bodies, dense vegetation, and urbanization can create suitable habitats for mosquitoes to thrive. Additionally, climate change and fluctuations in temperature and rainfall patterns can influence the distribution and abundance of mosquito species, ultimately affecting the transmission of diseases.
Lifecycle And Habits Of Disease Vectors
Understanding the lifecycle and habits of disease vectors, such as mosquitoes, is crucial in combating the spread of mosquito-borne diseases. Mosquitoes have a complex lifecycle consisting of four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Each stage plays a significant role in their feeding and breeding patterns, as well as their ability to transmit diseases.
Mosquito Feeding And Breeding Patterns
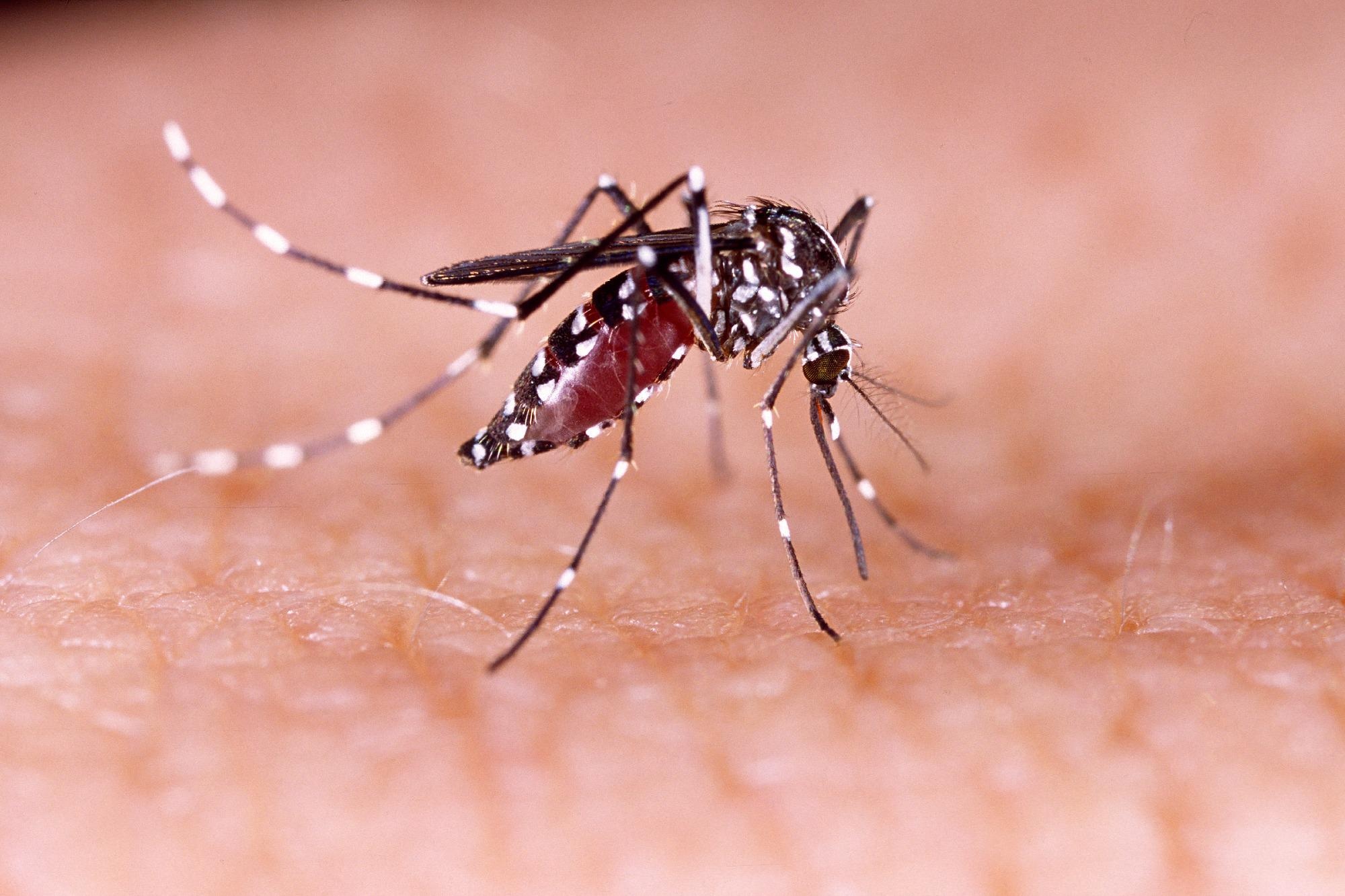
Mosquitoes are notorious for their feeding habits, with females being the primary culprits. Female mosquitoes feed on the blood of humans and animals, as they require the proteins found in blood to produce eggs. These blood meals are essential for their reproductive cycle. Mosquitoes are attracted to their hosts through various factors such as body odor, carbon dioxide, heat, and movement. Once they have located a suitable host, they use their proboscis to pierce the skin and extract blood.
In terms of breeding patterns, mosquitoes lay their eggs in stagnant water sources such as ponds, puddles, and containers. The eggs hatch into larvae, commonly known as wigglers, which live in the water and feed on organic matter. Larvae then develop into pupae, which are inactive and do not feed. After a few days, adult mosquitoes emerge from the pupae, ready to continue their life cycle.
The Role Of Mosquito Lifespan In Disease Spread
The lifespan of mosquitoes varies depending on the species, environmental conditions, and availability of food sources. On average, adult mosquitoes live for a few weeks to a few months. This relatively short lifespan is crucial in the transmission of diseases.
When a mosquito becomes infected with a disease-causing pathogen, such as a virus or parasite, it takes time for the pathogen to replicate within the mosquito’s body. Once the replication process is complete, the mosquito becomes capable of transmitting the disease to a new host. This transmission occurs when the infected mosquito takes a blood meal from an uninfected individual.
The lifespan of a mosquito directly affects its potential to transmit diseases. If a mosquito lives longer, it has a higher chance of biting multiple hosts and spreading the pathogen to more individuals. Conversely, if the lifespan is shorter, the window of opportunity for disease transmission is limited.
It is important to note that not all mosquitoes carry diseases. Only certain species are known to be vectors for specific pathogens. For example, Aedes mosquitoes are responsible for transmitting diseases such as dengue, Zika, and chikungunya, while Anopheles mosquitoes are known for transmitting malaria. Understanding the specific habits and lifecycles of disease-carrying mosquito species can help in implementing targeted control measures.
In conclusion, the lifecycle and habits of disease vectors, particularly mosquitoes, play a significant role in the spread of mosquito-borne diseases. By understanding their feeding and breeding patterns, as well as the impact of their lifespan on disease transmission, we can develop effective strategies to mitigate the risks associated with these disease vectors.

Credit: www.scientificamerican.com
Most Common Diseases Transmitted By Mosquitoes
Mosquitoes are not just pesky insects; they are also carriers of some of the most dangerous diseases known to humankind. The transmission of these diseases occurs when a mosquito feeds on the blood of an infected person and then bites someone else, passing on the infection. Below, we will explore some of the most common diseases transmitted by mosquitoes and their global impact.
Malaria And Its Global Impact
Malaria is a life-threatening disease caused by parasites that are transmitted to people through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), in 2019, there were an estimated 229 million cases of malaria worldwide, with an estimated 409,000 deaths. The majority of these cases and deaths occurred in the African region.
Zika, Dengue, And Chikungunya Explained
These diseases, caused by viruses transmitted primarily by Aedes mosquitoes, have become a growing concern due to their rapid spread and potential impact on public health. Zika virus infection during pregnancy can cause infants to be born with microcephaly and other congenital malformations. Dengue fever, a flu-like illness, can develop into a severe form of the disease, leading to hemorrhage, shock, and even death. Chikungunya causes fever and severe joint pain, and in some cases, can become a long-term, debilitating condition.
Understanding Transmission Dynamics
Transmission dynamics play a crucial role in understanding how often mosquitoes carry diseases. Mosquitoes can transmit various diseases like malaria, dengue, and Zika, making it essential to take precautions to prevent bites and potential infections.
How Mosquitoes Transmit Diseases
Mosquitoes transmit diseases through the bite of an infected female mosquito.
Factors Influencing Disease Transmission Rates
The transmission rates of diseases by mosquitoes are influenced by factors such as:
- Presence of the disease in the mosquito population
- Mosquito species and their feeding habits
- Environmental conditions affecting mosquito breeding
- Immune status and health of the host
Symptoms And Health Concerns
Mosquitoes can carry diseases such as malaria, dengue, West Nile virus, chikungunya, yellow fever, and Zika. If you develop severe swelling, pain, or itching after a bite, contact your healthcare provider. Mosquitoes are capable of biting multiple times in a night and can transmit diseases to humans.
Symptoms and Health ConcernsMosquito-borne diseases can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe. Some infected individuals may not experience any symptoms at all, while others may develop life-threatening complications. It’s important to recognize the symptoms of mosquito-borne diseases and seek medical attention if needed.Recognizing Mosquito-Borne Disease SymptomsThe symptoms of mosquito-borne diseases can vary depending on the type of virus transmitted. Common symptoms include fever, headache, body aches, joint pain, and rash. In severe cases, infected individuals may experience neurological symptoms such as confusion, seizures, or paralysis. Dengue fever, for example, can cause severe joint and muscle pain, while West Nile virus can lead to meningitis or encephalitis.When to Seek Medical AttentionIf you experience any symptoms after being bitten by a mosquito, it’s important to seek medical attention. In some cases, the symptoms may be mild and can be treated with rest and over-the-counter medications. However, if you experience severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing, chest pain, or severe headache, seek medical attention immediately.Prevention is key when it comes to mosquito-borne diseases. Avoiding mosquito bites by wearing protective clothing and using insect repellent can help reduce the risk of infection. Mosquito control measures such as removing standing water from your property can also help prevent the spread of mosquito-borne diseases.In conclusion, recognizing the symptoms of mosquito-borne diseases and seeking medical attention when needed is crucial for preventing severe complications. Taking steps to prevent mosquito bites can also help reduce the risk of infection.Prevention And Protection Strategies
Mosquito-borne diseases are a significant concern, and it’s crucial to implement effective prevention and protection strategies to minimize the risk of contracting these illnesses. By understanding the potential health hazards associated with mosquito bites, individuals can take proactive measures to safeguard themselves and their communities.
Effective Mosquito Repellents And Their Use
When spending time outdoors, it’s essential to use mosquito repellents that have been proven effective in warding off these disease-carrying insects. Products containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus are highly recommended for their ability to provide lasting protection against mosquitoes. It’s important to follow the instructions on the repellent’s label and reapply it as needed, especially if engaging in outdoor activities for an extended period.
Community And Government Mosquito Control Programs
Community and government mosquito control programs play a pivotal role in minimizing the prevalence of mosquitoes and reducing the risk of disease transmission. These programs often involve surveillance, larvicide application, and adult mosquito control measures to manage mosquito populations and mitigate the spread of diseases. By supporting and participating in these initiatives, individuals can contribute to the overall health and safety of their communities.
Credit: www.news-medical.net
The Future Of Mosquito-borne Diseases
Advances In Mosquito Control Technology
Mosquito-borne diseases are a significant global health concern, but advances in mosquito control technology offer hope for the future. Innovations such as genetically modified mosquitoes, targeted insecticides, and larval control methods are showing promise in reducing mosquito populations and curbing the spread of diseases.
Global Health Initiatives And Their Impact
Global health initiatives play a crucial role in combating mosquito-borne diseases. Collaborative efforts to improve surveillance, develop vaccines, and implement community-based interventions are making a tangible impact on disease prevention and control. By addressing the root causes of mosquito-borne illnesses, these initiatives are shaping a healthier future for vulnerable populations around the world.

Credit: m.facebook.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Odds Of Getting A Disease From A Mosquito?
Mosquitoes have the potential to transmit diseases such as malaria, dengue, West Nile virus, Zika, and yellow fever. However, not all mosquitoes carry diseases, and the likelihood of getting a disease from a mosquito bite depends on various factors such as geographical location and the prevalence of diseases in that area.
It is important to take preventive measures, such as using insect repellents and eliminating mosquito breeding sites, to reduce the risk of contracting a disease from mosquitoes.
When Should You Worry About A Mosquito Bite?
If a mosquito bite causes severe swelling, pain, or trouble breathing, seek medical help immediately.
How Long Does A Mosquito Have To Bite To Transmit Disease?
A mosquito needs 8-12 days to transmit a disease after getting infected through a blood meal.
Conclusion
Mosquitoes are known to transmit deadly diseases such as malaria, dengue, West Nile virus, chikungunya, yellow fever and Zika. The frequency of mosquitoes carrying diseases depends on various factors such as the location, climate, and human behavior. However, it is always better to take necessary precautions and protect ourselves from mosquito bites to avoid the risk of contracting these diseases.
By maintaining cleanliness, using mosquito repellents and nets, and seeking medical attention if necessary, we can prevent the spread of mosquito-borne illnesses. Stay safe and healthy!
Related posts:

I’m MD Tanvir, and I bring years of expertise gained from working closely with pest control companies to the forefront. My journey in the industry has inspired me to launch Bug Battler, a platform aimed at equipping people with the know-how to combat pests autonomously. Through Bug Battler, I aim to empower individuals with practical insights to tackle pest infestations effectively.