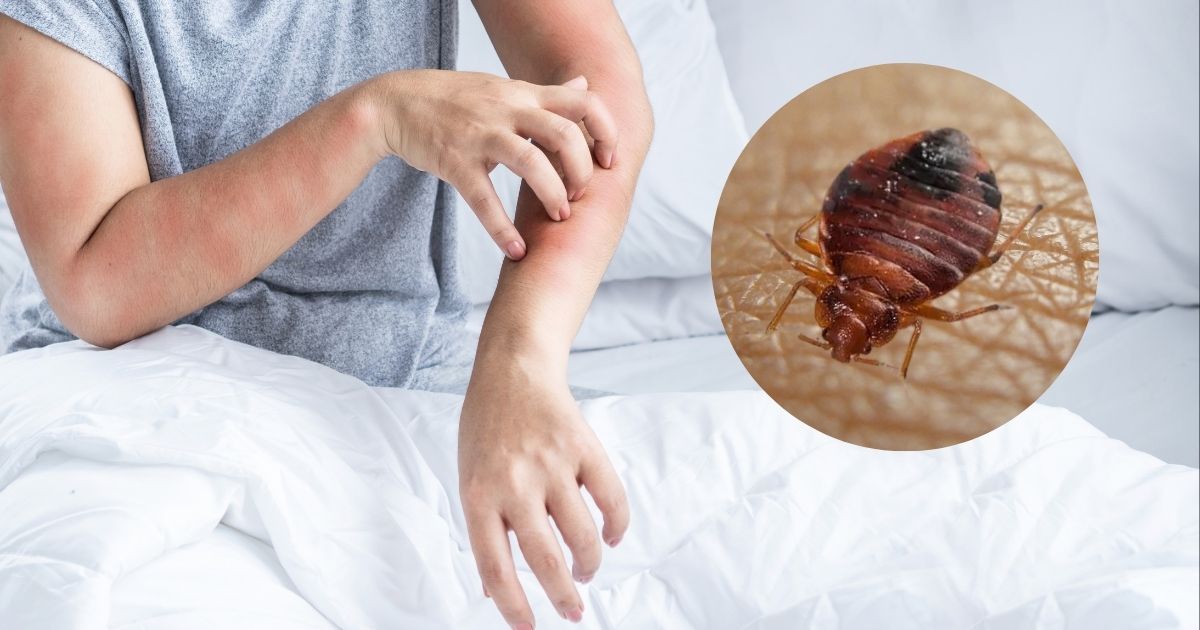
Bed bugs need to feed every 5 to 10 days to survive. Bed bugs depend on blood for their survival, and they typically need to feed every 5 to 10 days.
This feeding pattern is crucial for their reproduction and overall survival. Knowing how often bed bugs need to feed can help in implementing effective strategies to control and eliminate infestations in homes and other establishments. Understanding their feeding habits can also assist in identifying early signs of an infestation, providing insight into how to prevent their spread and establish effective pest management practices.
We will delve into the feeding habits of bed bugs and explore the significance of regular feeding for their existence.
Bed Bug Feeding Habits
Bed bugs are notoriously resilient pests that can cause a multitude of problems for homeowners. Understanding their feeding habits is essential for effectively dealing with an infestation. Here, we’ll delve into the blood feeding behavior and frequency of feeding of these persistent parasites.
Blood Feeding Behavior
Bed bugs are exclusively blood-feeding insects, relying on the blood of hosts for their survival. Their feeding behavior involves piercing the skin of their host with their elongated mouthparts and extracting the blood. Once engorged, they retreat to a secluded hiding place to digest the blood meal and molt to the next stage of their lifecycle.
Frequency Of Feeding
Bed bugs require regular blood meals to survive and reproduce. Typically, adult bed bugs can survive for several months without a blood meal, while nymphs (young bed bugs) require a blood meal more often to molt and progress to the next stage. Under favorable conditions, bed bugs may feed every 3-7 days. However, in unfavorable conditions, such as low temperatures, they can go into a state of dormancy and survive for long periods without feeding.

Credit: www.scientificamerican.com
Survival Tactics
Bed bugs are resilient pests that can survive for several months without a blood meal. These parasites need to feed on blood at least once every 14 days to survive and complete their life cycle. Understanding their feeding habits is crucial for effective pest control and prevention strategies.
Survival TacticsAdaptations For Survival
Bed bugs have adapted to survive by being excellent hitchhikers, moving from one place to another. Their flat bodies enable them to hide in cracks and crevices, making them hard to detect. Adapting to various environments, bed bugs can go for months without feeding.Effects Of Feeding Frequency On Longevity
Regular feeding is essential for the longevity of bed bugs. Frequent blood meals ensure their survival and reproduction. Bed bugs that feed more often tend to live longer than those deprived of blood meals, which can impact their ability to reproduce.In summary, bed bugs have developed unique adaptations for survival, including their ability to go long periods without feeding. However, regular blood meals are crucial for their longevity and reproductive success.Factors Influencing Feeding Frequency
Bed bugs’ feeding frequency is influenced by various factors such as temperature, availability of hosts, and their developmental stage. These pests typically need to feed every few weeks to survive, but they can go for several months without feeding if necessary.
Factors Influencing Feeding FrequencyWhen it comes to bed bugs, understanding their feeding habits is crucial in combating these pesky parasites. Bed bugs rely on blood meals to survive and reproduce, but how often do they actually need to feed? The answer depends on various factors that influence their feeding frequency. By exploring these factors, we can gain insights into the behavior and survival tactics of bed bugs.Environmental factors play a vital role in determining how often bed bugs feed. These factors include the availability of hosts, temperature, and access to suitable harborage. If the environmental conditions are favorable, bed bugs will have more opportunities to feed and reproduce. However, adverse conditions such as extreme temperatures or lack of suitable hiding spots can limit their feeding frequency.Life stage is another crucial factor that influences bed bug feeding frequency. Bed bugs go through several developmental stages, starting from eggs to nymphs and finally becoming adults. During each stage, bed bugs require a blood meal to molt and progress to the next stage. As nymphs, they often need to feed more frequently compared to adults. This increased feeding frequency is essential for their growth and development.To summarize, environmental factors and life stage significantly impact the feeding frequency of bed bugs. Understanding these factors can aid in devising effective strategies to control and eliminate bed bug infestations. Whether it’s ensuring optimal temperature conditions or targeting nymphs during treatment, tailoring our approach based on these factors can increase the likelihood of successfully eradicating these unwanted guests. In the next sections, we will delve deeper into each factor to gain a better understanding of their influence on bed bug feeding habits.H3: Environmental factorsSeveral environmental factors affect bed bug feeding frequency. These factors include:1. Availability of hosts: Bed bugs primarily feed on human blood, but they can also feed on other warm-blooded animals. The presence of a constant source of blood nearby, such as humans or pets, increases the opportunities for bed bugs to feed.2. Temperature: Bed bugs thrive in temperate environments, with an optimal temperature range of 70 to 80 degrees Fahrenheit. Cold temperatures can slow down their metabolism and feeding activity, while extreme heat can be fatal to them.3. Harborage availability: Bed bugs seek shelter in cracks, crevices, and other hiding spots during non-feeding periods. Adequate harborage availability allows them to hide and reproduce, ultimately increasing their chances of finding hosts to feed on.By considering these environmental factors, we can gain insights into the feeding patterns of bed bugs and implement targeted control measures to disrupt their life cycle. Let’s now explore the impact of life stage on their feeding frequency.H3: Life stageBed bugs go through five nymphal stages before reaching adulthood. During each nymphal stage, they require a blood meal to molt into the next stage. The frequency of feeding varies depending on the nymphal stage:1. First-stage nymphs: These young nymphs typically feed more frequently than older nymphs or adults. They require a blood meal every few days to fuel their rapid growth.2. Second to fifth-stage nymphs: As nymphs mature, they may exhibit less frequent feeding intervals, ranging from once a week to every few weeks, depending on food availability and environmental conditions.3. Adult bed bugs: Once bed bugs reach adulthood, they can survive for several months without a blood meal. However, if provided with regular access to hosts, they will continue to feed approximately once a week.Understanding the feeding frequency of bed bugs at each life stage is crucial for implementing effective control strategies. By targeting the nymphs, which have a higher feeding requirement, we can disrupt their life cycle and prevent the onset of new infestations.In conclusion, various factors influence the feeding frequency of bed bugs. Environmental factors such as host availability, temperature, and harborage availability, along with the bed bugs’ life stage, play a significant role in determining how often they feed. By considering these factors, we can develop targeted approaches to control and eradicate bed bug infestations efficiently.
Credit: www.terminix.com
Impact On Infestations
Bed bugs are nocturnal pests that feed on the blood of humans and animals to survive. Understanding their feeding habits is crucial in combating infestations effectively. The frequency at which bed bugs need to feed has a direct impact on how quickly an infestation can grow and spread. Let’s explore the link between feeding frequency and infestation growth, as well as strategies for controlling and eliminating these pesky bugs.
Link Between Feeding Frequency And Infestation Growth
Bed bugs are notorious for their rapid reproductive rates. A single female bed bug can lay hundreds of eggs throughout her lifetime, leading to exponential population growth if left unchecked. The rate at which an infestation grows depends on several factors, including the frequency at which bed bugs need to feed.
Bed bugs typically feed every five to ten days, although they can go without feeding for several months under ideal conditions. The feeding frequency of bed bugs is influenced by various factors, such as room temperature, availability of hosts, and the bug’s developmental stage.
Feeding frequency can affect infestation growth in the following ways:
- Rapid Population Increase: The more often bed bugs feed, the quicker they can mate and reproduce. This leads to a higher number of eggs being laid and a faster growth rate of the infestation.
- Survival and Longevity: Regular blood meals provide bed bugs with the necessary nutrients to survive and thrive. When deprived of feeding opportunities, bed bugs can enter a state of hibernation or become more aggressive in their search for new hosts, making them harder to eliminate.
- Migration and Spread: Bed bugs that feed infrequently may have to search for new hosts more often, increasing the chances of them hitchhiking on clothing, luggage, or other items and spreading to new areas.
- Resistance to Control Measures: Bed bugs that feed less frequently are more likely to come into contact with insecticides or other control methods, potentially developing resistance over time. This makes it crucial to address infestations as soon as they are detected, regardless of the feeding frequency.
Strategies For Controlling Infestations
Controlling bed bug infestations requires a multifaceted approach that targets both adult bugs and their eggs. Here are some effective strategies to consider:
- Professional Pest Control: Hiring a professional pest control company that specializes in bed bug treatments can be the most effective and efficient way to eliminate an infestation. These experts have the knowledge, experience, and tools to find and treat all hiding spots, ensuring comprehensive eradication.
- Thorough Cleaning and Decluttering: Regularly vacuuming, sweeping, and decluttering your living areas can help reduce hiding spots for bed bugs, making it easier to detect and eradicate them. Be sure to seal and dispose of vacuum bags properly to prevent reinfestation.
- Washing and Drying: Launder all infested clothing, bedding, and fabrics using hot water and high heat in the dryer. This kills both bed bugs and their eggs. Consider using mattress and box spring encasements to seal any remaining bed bugs inside and prevent them from feeding or reproducing further.
- Insecticide Treatments: When used correctly and in conjunction with other control methods, insecticides can be effective in treating bed bug infestations. However, it is essential to follow the product instructions carefully and consider seeking professional advice for safe and successful application.
- Preventive Measures: To minimize the risk of future infestations, take precautionary measures such as regularly inspecting hotel rooms and second-hand furniture, sealing cracks and crevices, and using mattress encasements to keep bed bugs at bay.
Remember that early detection and immediate action are key to preventing the rapid growth and spread of bed bug infestations. By understanding their feeding frequency and implementing effective control strategies, you can protect your home and sleep soundly without the presence of these unwelcome nuisances.
Health Implications
Bed bugs require regular blood meals to survive, posing health risks to individuals they feed on. Understanding the implications of their feeding habits is crucial in preventing potential health issues.
Risks Associated With Frequent Feeding
- Constant itching and discomfort: Frequent bites lead to persistent itching and discomfort, affecting quality of life.
- Skin infections: Continuous feeding can result in skin infections due to scratching and open wounds.
- Allergic reactions: Some individuals may develop allergic reactions to bed bug saliva, causing further health complications.
Transmission Of Diseases
- Pathogen carriers: Bed bugs can act as carriers of pathogens, increasing the risk of disease transmission.
- Blood-borne illnesses: The feeding process creates an opportunity for the transmission of blood-borne illnesses from one host to another.
- Psychological impact: Dealing with a bed bug infestation can have psychological effects, leading to stress and anxiety.
Managing Bed Bug Feeding
Preventive Measures
One of the crucial aspects of managing bed bug feeding is to employ effective preventive measures. To reduce the risk of infestation, it’s essential to seal any cracks and crevices in walls, furniture, and baseboards. Regularly clean and declutter living spaces and encase mattresses and box springs with bed bug-proof covers. Additionally, inspect second-hand furniture before bringing it into your home, as this can be a common source of infestation.
Treatment Options
When it comes to addressing bed bug infestations, there are various treatment options available. Professional pest control services can provide powerful solutions including chemical treatments, heat treatment, and vacuuming. For a more natural approach, diatomaceous earth and steam treatments can also be effective. It’s important to consult with a professional to determine the best course of action for your specific situation. By following these suggestions, you can effectively manage bed bug feeding and minimize the risk of infestation.
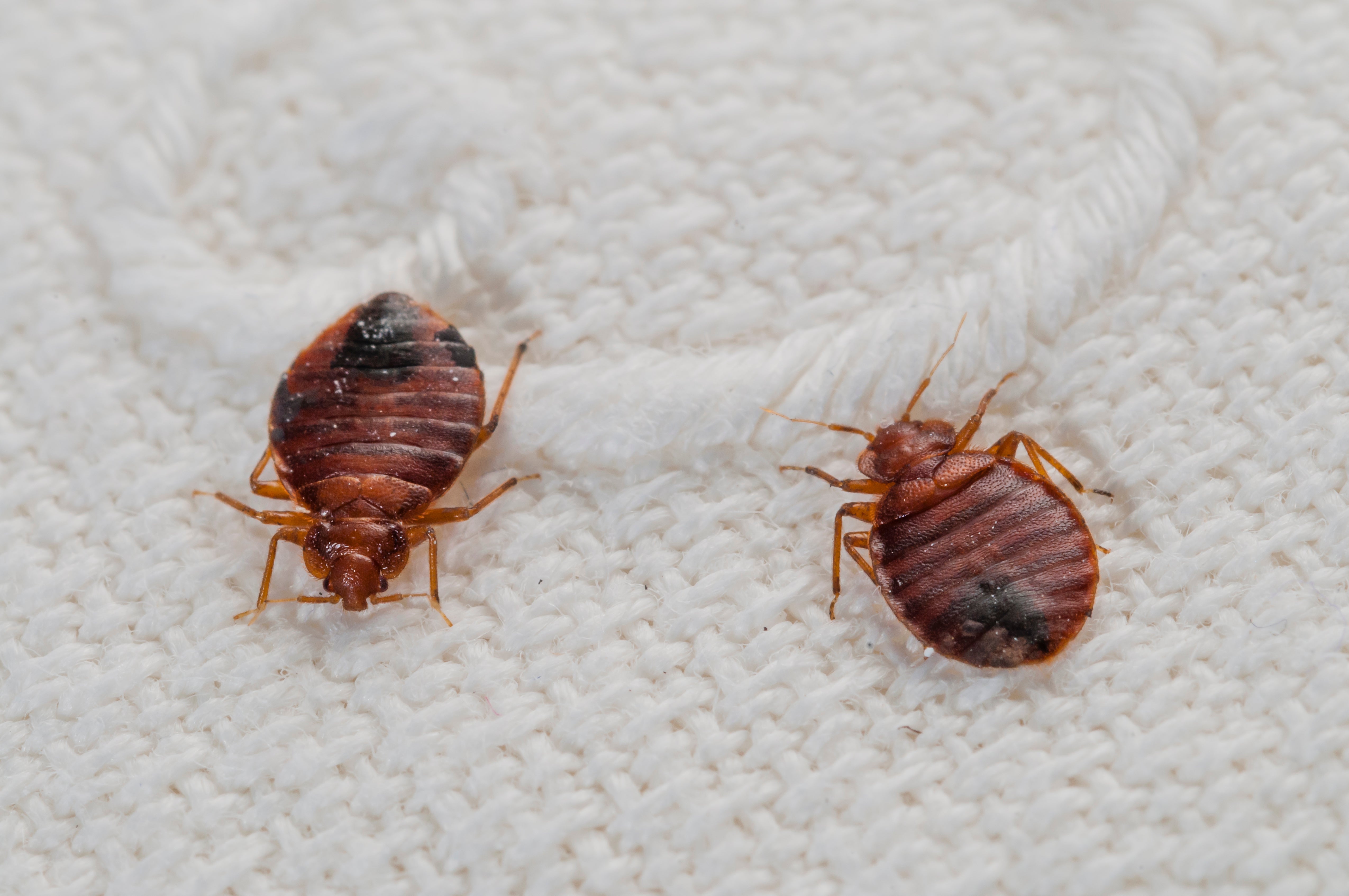

Credit: www.scientificamerican.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of How Often Do Bed Bugs Need To Feed To Survive?
How Often Do Bed Bugs Feed In Order To Survive?
Bed bugs feed on blood about once every 5 to 10 days in order to survive and reproduce. However, they can live for several months without feeding if necessary. Their feeding frequency may vary depending on factors such as temperature, availability of hosts, and their life stage.
Conclusion
In understanding bed bugs’ feeding habits, regular meals keep them thriving. Consistent access to blood is vital for their survival. Knowing how often they feed aids in effective pest control strategies. By disrupting their feeding cycles, it’s possible to manage and eliminate bed bug infestations successfully.
Related posts:

I’m MD Tanvir, and I bring years of expertise gained from working closely with pest control companies to the forefront. My journey in the industry has inspired me to launch Bug Battler, a platform aimed at equipping people with the know-how to combat pests autonomously. Through Bug Battler, I aim to empower individuals with practical insights to tackle pest infestations effectively.