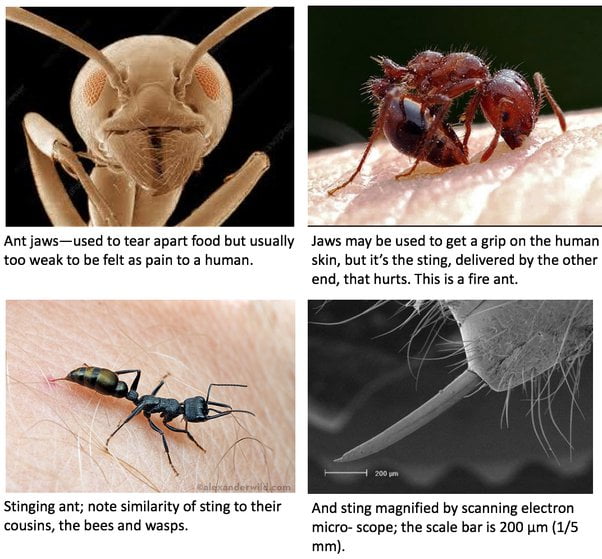
Ant venom can be deadly, although it largely depends on the species and the victim’s allergic reactions. Most ant stings cause minor irritation, but some, like the bullet ant, can cause severe pain.
Ants, often perceived as mere nuisances, do have a menacing side. Their venom, evolved for defense and predation, has varying effects on humans. The stings from common species typically result in itching and discomfort. Yet, certain ants pack a potent punch.
The bullet ant, named for a sting as painful as a gunshot, can incapacitate a person with its venom. Another feared species is the fire ant, whose venom can trigger anaphylactic shock in allergic individuals. Although fatalities are exceedingly rare, the risk is significant enough to warrant caution around these tiny but formidable creatures. Understanding the potential danger is crucial, particularly for those with known allergies to insect stings, highlighting the importance of recognizing and avoiding hazardous ant species.
Credit: www.quora.com
The Lethal Potentials Of Ant Venom
Imagine a creature so small yet with a sting that could take down giants. Ants might be tiny, but their venom packs a punch. While not all ants are dangerous, some species have venom that is potent enough to cause serious harm to humans. Understanding the lethal potentials of ant venom is essential. This knowledge can help us respect and avoid the unnecessary pain they can inflict.
The Composition Of Ant Venom
Ant venom is a complex chemical cocktail. It is designed to protect these tiny insects from predators. The main component in many ant venoms is formic acid. Some also contain proteins and peptides that can affect the victim’s cells and nerves. Here’s what these components do:
- Formic Acid: Causes pain and irritation at the sting site.
- Proteins and Peptides: Can disrupt nerve signals and damage tissues.
While most people experience minor reactions, those allergic to ant venom may face severe consequences.
Comparison With Other Venoms
When we compare ant venom with other venoms, we notice striking differences. The venom from snakes or spiders often gets more attention. This is because they can be more deadly to humans. But let’s not underestimate the power of ant venom. To give you a clearer picture:
| Ant Venom | Snake Venom | Spider Venom |
|---|---|---|
| Less protein-rich | More protein-rich | Proteins and neurotoxins |
| Mainly formic acid | Contains hemotoxins and neurotoxins | Can cause cell death and paralysis |
| Causes pain and irritation | Can lead to systemic effects | Effects vary widely across species |
In terms of lethality, snake and spider venoms can be more dangerous. However, certain ant venoms, specifically from the fire ant (Solenopsis spp.), can also be lethal. When multiple stings occur or the victim has an allergic reaction, the result can be fatal.

Credit: www.medicalnewstoday.com
Myths Vs. Facts About Ant Stings
Ant stings are a common outdoor nuisance, but how dangerous are they? While stories and hearsay often exaggerate the risks, it’s crucial to separate fiction from reality. Let’s debunk some myths and validate what science says about ant venom and its effects on humans. Understanding these facts can help minimize panic and ensure proper response to ant encounters.
Popular Ant Venom Myths
Many myths surround ant stings and their potential to cause harm. Fear often stems from tales of deadly ant encounters. First and foremost, not all ants have venom. Even those with venom don’t carry enough to kill a human. One popular myth is that all ant stings can lead to anaphylactic shock. This is extremely rare and generally occurs in sensitive individuals.
Scientifically Proven Effects
Now, let’s look at what research has revealed about ant stings. Some ants, such as the fire ant, inject venom that can cause a painful sting. The effect usually involves redness, swelling, and a burning sensation. In confirmed cases of allergic reactions, symptoms can escalate to dizziness and shortness of breath. The Bullet ant, with its potent sting, will cause intense pain. However, the venom it uses for defense is not lethal for humans.
If an ant sting causes concern or allergic symptoms appear, seek medical help immediately. Always keep in mind, most ant stings are harmless and manageable with basic first aid.
The Deadliest Ants On The Planet
Ants may seem small, but some pack a deadly punch. Their venom can knock out predators much larger than themselves. Only a few have a sting potent enough to kill a human. Let’s unmask these tiny assassins.
Bullet Ants: Nature’s Pain Inducers
The bullet ant sits at the pinnacle of insect-induced agony. Its venomous sting rivals a gunshot wound. Indigenous to Central and South America, they are hard to miss. Their sting causes intense pain that can last for over 24 hours.
- Scientific Name: Paraponera clavata
- Sting Pain Duration: 24 hours
- Size: Up to 1.2 inches long
- Habitat: Rainforests
The Fearsome Fire Ant
Fire ants are notorious. They sting in unison when their nests are disturbed. Found mostly in warm climates, these ants inject a toxin that can be lethal. Allergic reactions to their stings have caused fatalities.
| Feature | Detail |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Solenopsis |
| Sting | Sharp pain and swelling |
| Size | 0.08 to 0.24 inches |
| Habitat | Moist areas near food sources |
Human Encounters With Ant Venom
Ant venom has a notorious reputation among those who’ve felt its sting. These tiny creatures pack a forceful punch with their venom, leading to natural curiosity about its potency. Can an ant’s defense mechanism, intended to protect it from predators, pose a life-threatening hazard to humans? Let’s delve into the tales and data surrounding human encounters with ant venom to find the answer.
First-hand Accounts Of Ant Stings
Bold adventurers and unlucky souls alike have shared their experiences with ant stings. Common symptoms reported by sting recipients include:
- Sharp pain that increases rapidly
- Redness and swelling at the sting site
- A burning sensation
- Possible allergic reactions in some individuals
Fire ants, known for their aggressive stings, often attack en masse which can lead to an overwhelming number of painful welts. Personal accounts highlight the importance of avoiding ant nests and seeking medical attention immediately if symptoms escalate.
Medical Records Of Ant Venom Incidents
Medical literature provides a structured view of how ant venom affects humans. Various documented cases note:
| Type of Ant | Reaction Severity | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Bullet Ant | Moderate to Severe | Intense Pain, Rarely Fatal |
| Fire Ant | Mild to Moderate | Itching, Anaphylaxis (Rare) |
| Jack Jumper Ant | Moderate to Severe | Allergic Reactions, Potentially Fatal |
Although fatalities from ant stings are rare, each sting deserves attention and care. Records emphasize that individuals with hypersensitivity to venom present the highest risk and may require rapid medical intervention. Preventative measures, including avoiding known habitats and wearing protective clothing, are crucial to minimize the chances of an ant venom encounter turning deadly.
How Ant Venom Affects The Human Body
The impact of ant venom on the human body can range from a mild irritation to severe health consequences. Ant stings inject venom that contains a mix of toxins, proteins, and chemicals. Understanding how this venom affects us is critical for both first aid and long-term health management.
Immediate Physiological Reactions
Upon an ant sting, the body immediately reacts to the venom. The main symptoms are:
- Sharp pain at the sting site
- Redness and swelling may follow
- Itching and burning sensations are common
Some people may experience an allergic reaction. Symptoms include:
- Rapid swelling around the eyes and lips
- Difficulty breathing
- Dizziness or fainting
If these occur, seek medical help immediately. Time is important to prevent serious complications.
Long-term Health Implications
The long-term effects of ant venom are usually less severe but can include:
| Type of Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Allergic Sensitization | Increased likelihood of allergic reactions with future stings. |
| Skin Infections | Scratching can introduce bacteria, leading to infection. |
| Nerve Damage | Rare but possible if venom affects nervous tissue. |
Monitoring the sting area for signs of infection or prolonged pain is key to managing long-term risks. Seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen.
Treatment And First Aid For Ant Stings
When it comes to ant stings, timely treatment and first aid can make all the difference. While most ant stings are harmless, certain species can pack a potent punch. Understanding the immediate actions to take and when to seek medical attention is crucial for safety.
Immediate Response To Ant Stings
The steps below should be taken right after an ant sting:
- Remain Calm: Staying still prevents further stings.
- Remove Ants: Gently brush ants off the skin.
- Clean the Area: Wash with soap and water.
- Apply Ice: A cold pack reduces swelling and pain.
- Topical Treatments: Use creams or lotions to soothe the sting.
- Elevate the Area: This can lessen swelling.
Seeking Professional Medical Help
Here is when to seek immediate medical attention:
| Symptom | Action |
|---|---|
| Breathing Difficulties | Call emergency services right away. |
| Swelling in Throat or Tongue | Medical emergency; needs immediate help. |
| Rapid Heart Rate | Seek urgent medical attention. |
| Dizziness or Confusion | Indicates possible allergic reaction; get help. |
| Large Area of Swelling | If swelling spreads, visit a doctor. |
| Hives or Rash Developing | Contact a professional; may be an allergy. |
Note: Individuals with known allergies should carry epinephrine auto-injectors.
Remember: Prompt action can prevent complications from ant stings.
Prevention Better Than Cure
The phrase ‘Prevention Better than Cure’ perfectly fits when talking about the risks of ant venom. While most ant stings are harmless, certain species can pose serious health threats. Recognizing the potential danger is the first step to ensuring your safety.
Avoiding Ant Inhabited Areas
Knowledge of your environment serves as a shield against ant-related incidents. Explore nature, but stay aware of your surroundings. Recognize ant nests and steer clear to reduce the risk of stings. Remember, ants protect their homes.
- Observe ground for ant pathways.
- Steer clear of ant mounds.
- Avoid picnics near ant hotspots.
Protective Measures Against Ants
Safeguarding yourself is simple with the right techniques. Long clothing guards your skin, while insect repellent can deter ants. Check for ants before sitting or lying on the ground. Ensure food containers are sealed tight. This way, you minimize the allure for ants.
- Wear long sleeves and pants.
- Use ant repellent.
- Check gear for ants regularly.
- Keep snacks in ant-proof containers.
Research At The Forefront
Ant venom can be both a potent weapon and a medical marvel. Under the microscope, researchers explore its secrets. Their aim? To pioneer breakthroughs in science and healthcare. The quest to understand ant venom unlocks a realm of possibilities, from painkillers to life-saving drugs. This journey takes us to a thrilling edge of biological research.
Studying Ant Venom For Medical Uses
Ant venom contains powerful compounds. Scientists are eager to harness these elements for medical treatments. Tiny yet mighty, ants offer clues to developing new medicines. Labs buzz with activity, as research teams isolate venom components to treat diseases and manage pain.
- Identifying pain-blocking properties in venom peptides.
- Testing anti-inflammatory effects on chronic conditions.
- Exploring venom’s potential to fight bacterial infections.
Each discovery is a step toward innovative therapies that could revolutionize modern medicine.
Developing Antivenom: Progress And Challenges
Rising to the challenge, scientists work to create antivenoms. These antivenoms aim to neutralize dangerous stings and save lives. The development pipeline is complex and requires significant resources.
| Stage | Progress | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Research | Isolating active venom components. | Limited funding and resources. |
| Testing | Ensuring antivenom effectiveness and safety. | Technical hurdles and ethical considerations. |
| Approval | Securing regulatory green light. | Strict standards and lengthy evaluation processes. |
Despite these hurdles, progress marches on. Teams globally collaborate, sharing findings to advance antivenom research at a remarkable pace.

Credit: www.fireants.org.au
Frequently Asked Questions For Can Ant Venom Kill You
How Deadly Is Ant Venom?
Ant venom can be irritating, but it’s rarely deadly to humans. Some species like the bullet ant can cause extreme pain. However, allergic reactions can indeed be serious and potentially life-threatening.
Can Fire Ant Bites Be Fatal?
For most people, fire ant bites cause discomfort, not death. Those with severe allergies to the venom, though, may experience anaphylaxis, which could be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
What Symptoms Do Ant Venoms Cause?
Symptoms of ant venom include pain, redness, swelling, and itching at the sting site. Severe reactions may involve difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, or swelling of the throat and face.
Which Ant Has The Most Potent Venom?
The Maricopa harvester ant is known for having one of the most potent venoms among ants. Its venom is more toxic than that of rattlesnakes, but the small quantity injected means it’s less dangerous to humans.
Conclusion
Ant venom can invoke fear, yet for most, it poses little threat. Rarely, severe reactions can occur, and caution is advised. Staying informed about ant species and their effects arms you with knowledge to prevent tragic encounters. Remember, ant venom fatalities are exceptional, not the norm.
Stay safe and aware.

I’m MD Tanvir, and I bring years of expertise gained from working closely with pest control companies to the forefront. My journey in the industry has inspired me to launch Bug Battler, a platform aimed at equipping people with the know-how to combat pests autonomously. Through Bug Battler, I aim to empower individuals with practical insights to tackle pest infestations effectively.