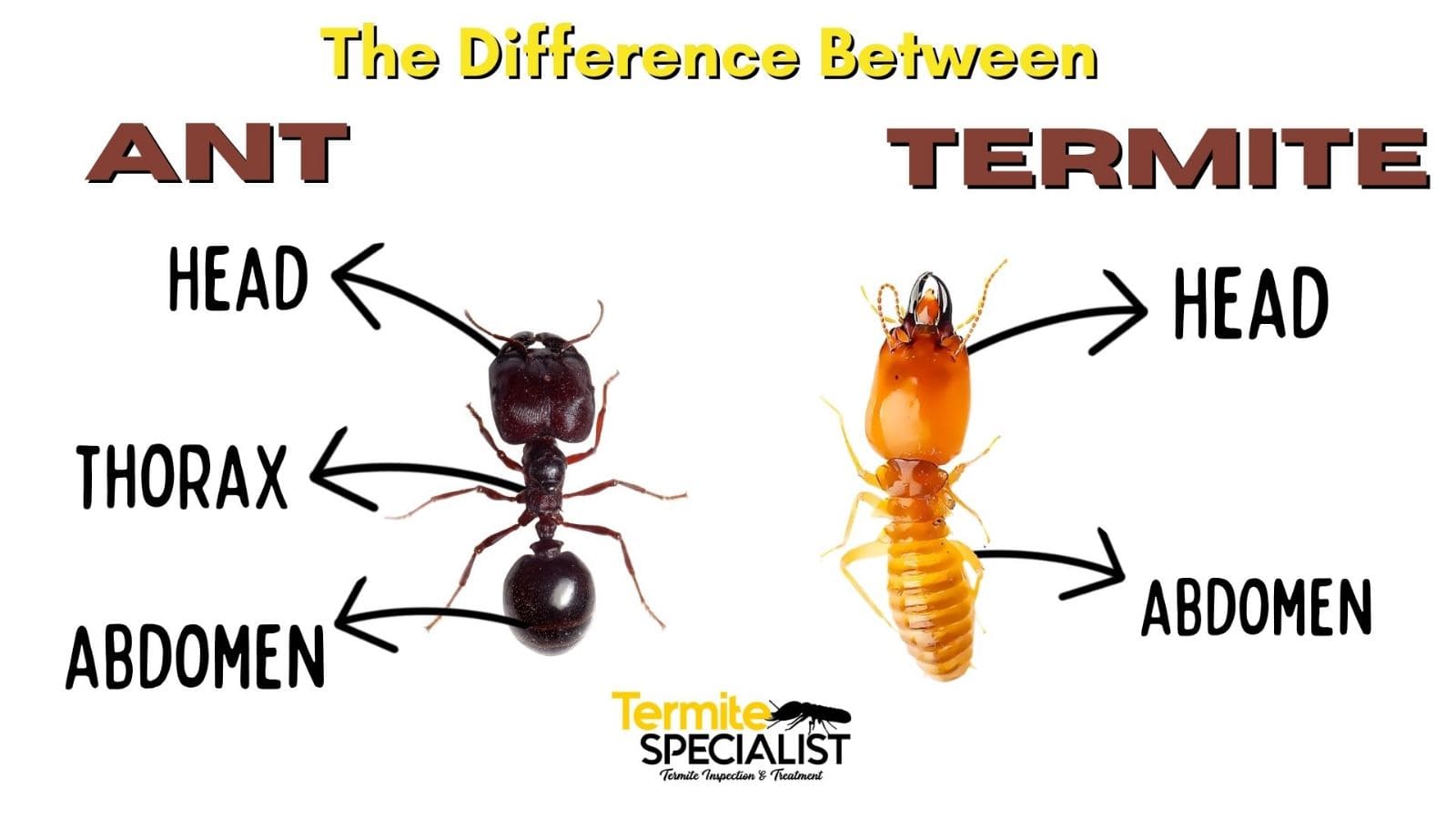
Ants and termites are both social insects but have distinct characteristics and behaviors. Ants typically have a narrow waist and elbowed antennae, while termites have a broad waist and straight antennae.
Ants are known for their strong jaws and ability to communicate through pheromones, while termites are expert builders that feed on wood. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective pest control measures. Let’s delve deeper into the unique features and behaviors of ants and termites in order to better differentiate between the two species and effectively manage them in various environments.
By recognizing their distinct traits, we can implement targeted strategies to address infestations and protect our homes and structures from damage.
Physical Characteristics
Physical characteristics play a crucial role in distinguishing ants from termites. Understanding these differences is essential for effective pest control and management. Let’s delve into the physical characteristics of both ants and termites to better comprehend their unique attributes.
Ant
Ants are identifiable by their distinct physical features. They typically have segmented bodies consisting of three parts: the head, thorax, and abdomen. With a pair of elbowed antennae and a narrow waist or petiole, ants are equipped for efficient movement and communication through the use of pheromones. These insects are usually winged during the mating season, making them more conspicuous to the human eye.
Termite
Termites possess physical traits that set them apart from ants. They, too, have segmented bodies consisting of the head, thorax, and abdomen. Unlike ants, termites do not have a distinct waist and their bodies are relatively straight in shape. Termites’ straight antennae and pale, soft bodies are notable features that differentiate them from ants. Additionally, termites are often winged during their reproductive stages, similar to ants.

Credit: www.angi.com
Habitat
Ants and termites have distinct habitats, with ants preferring warm climates and termites thriving in damp areas. Both insects build intricate structures—ant hills or termite mounds—to house their colonies. The habitat choice is crucial for the survival and prosperity of each species.
`ant`
`Ants create nests in various locations, such as underground, in rotten wood, or within structures.They prefer moist environments like gardens, lawns, and near food sources.``termite`
`Termites are mostly found in damp and warm areas and are commonly seen in close proximity to wood.Their colonies can be in trees, stumps, or within the wooden structures of homes.Ants primarily live on dry land and build their colonies in a variety of locations, while termites thrive in damp and warm environments, usually near wood sources.Behavior
In the battle of ant vs termite, behavior plays a vital role. Ants are known for their organized and cooperative behavior, while termites exhibit intricate communication and construction skills. Understanding the behavior of these insects is crucial in pest management strategies.
Ant
are both social insects that live in colonies, exhibiting distinct behaviors.Termite
Ants are highly organized with specific roles among members, whereas termites prioritize the colony as a whole. Ants use chemical signals to communicate and establish sophisticated hierarchical structures, whereas termites rely on pheromones to maintain social order. Ants are known for their aggressive behavior when defending their territory or foraging for food, while termites focus on building and maintaining their nest structure. Ants showcase varied behavior based on their species, such as army ants that work together to hunt or fire ants that aggressively protect their nest. Termites, on the other hand, are considered docile insects that prioritize the safety and sustainability of their colony above all else. In summary, ants are more aggressivecommunal approach within the colony.Nesting Habits
Nesting habits of ants and termites vary significantly, impacting their behavior, food sources, and potential damage to homes. Understanding the difference between the nesting habits of these two pests is crucial for effective pest control and prevention.
Ant
Ants, generally, establish their nests in soil or decaying wood, though some species may prefer to nest indoors. They construct extensive tunnel systems that can spread over wide areas. Both indoor and outdoor ant species create nests in various environments, making them adaptable and difficult to eliminate.
Termite
Termites are known for building extensive and sophisticated colonies within wood, soil, or even in structural components of buildings. They consume cellulose, a primary component of wood, and require a damp environment to thrive. This specific nesting habit enables them to cause substantial damage to wooden structures if left unchecked.
Diet
Discover the differences between ants and termites in terms of diet. While ants tend to consume a variety of foods including nectar and other insects, termites primarily feed on wood and other cellulose-based materials. Understanding their distinct dietary preferences is essential for effective pest control and management.
Ant
Ants are tiny insects that are known for their diverse diets. They are omnivorous creatures, meaning they eat a wide variety of foods. Their diet mainly consists of both plant and animal matter.While some species of ants are herbivorous, feeding primarily on leaves, flowers, and fruits, others are carnivorous, preying on other insects, spiders, and even small animals. Ants are also known to scavenge on dead animals and feed on sugary substances like nectar and honeydew.Ants have a unique way of obtaining food. They use their powerful mandibles to bite into their prey or chew on plant material. The carcass of their prey or the mashed plant material is then shared among the colony members, creating a cooperative and well-organized feeding system.Termite
Termites, on the other hand, have a highly specialized diet consisting mainly of cellulose. These insects are often referred to as “silent destroyers” due to their ability to feed on wood and other cellulose-based materials, causing significant damage to structures.Termites have developed a symbiotic relationship with microorganisms in their gut that enable them to break down cellulose into usable nutrients. This unique adaptation allows them to digest cellulose-rich materials, such as plant fibers and wood, which are typically indigestible for many other organisms.Unlike ants, termites are not aggressive predators. They mostly feed on dead wood, fallen leaves, and other plant debris, aiding in the decomposition process. However, in the case of subterranean termites, they can cause extensive damage to wooden structures if left unchecked.In summary, both ants and termites have their own distinctive diets. While ants have a more varied diet, consuming both plant and animal matter, termites specialize in feeding on cellulose-rich materials, such as wood. Understanding the diet of these fascinating insects helps us appreciate their role in the ecosystem.Social Structure
Ants and termites are both social insects, but they have distinct differences in their social structures.
Ant
Ants are known for their highly organized and complex societies. They live in colonies, which can range in size from a few dozen individuals to millions. Each ant colony consists of three main castes: the queen, the workers, and the males.
The queen is the mother of all the ants in the colony. Her primary role is to reproduce and ensure the survival of the colony. She can live for several years and lays thousands of eggs during her lifetime. The workers, which make up the majority of the colony, are responsible for various tasks such as gathering food, caring for the young, and building and maintaining the nest.
The males, also known as drones, are responsible for mating with the queen. Once they have fulfilled their purpose, they die shortly afterward. Ant colonies have a clear division of labor, with each caste having specific roles and responsibilities.
Termite
Like ants, termites also live in highly organized colonies. However, their social structure differs in several ways. Termite colonies consist of three main castes: the reproductives, the soldiers, and the workers.
The reproductives, similar to the ant queen, are responsible for reproduction. There are typically one or a few termite queens in each colony, and they can live for several years. The soldiers have the task of defending the colony against threats, such as predators or invading ants.
The workers, as the largest caste, are responsible for building and maintaining the nest, as well as gathering food and caring for the young. Unlike ants, termite workers can undergo molting, allowing them to take on different roles within the colony as needed.
Overall, while ants and termites have similar social structures with distinct castes, their specific roles and organization are unique to each species. Understanding these differences can provide valuable insights into their behavior and interactions within their respective colonies.
Economic Importance
The economic importance of ants and termites cannot be overstated. These insects play crucial roles in various ecosystems across the world, directly impacting human activities and industries. From agriculture to construction, ants and termites contribute to the balance of ecosystems and support human development in significant ways.
Ant
Ants are vital to ecosystems as they aid in the decomposition of organic matter, leading to nutrient recycling. In agricultural settings, ants help control pests and are instrumental in improving soil quality through their tunneling activities, enhancing overall crop growth and productivity.
Termite
Termites, on the other hand, significantly impact the construction and forestry sectors. While they are notorious for causing structural damage to buildings and wooden structures, termites also play a critical role in the decomposition of dead wood, aiding in the nutrient cycle of forests and contributing to the overall health of ecosystems.

Credit: www.evanspestmgmt.com

Credit: traplinepest.com
Frequently Asked Questions For Ant Vs Termite
What Is The Difference Between Ants And Termites?
Ants and termites are both social insects, but there are some key differences. Ants have a narrow waist, while termites have a broad waist. Ants have elbowed antennae, while termites have straight antennae. Ants primarily feed on foods high in protein, while termites feed on cellulose in wood.
How Do Ants And Termites Build Their Colonies?
Ants and termites both build elaborate colonies, but their methods differ. Ants create intricate networks of tunnels and chambers, constructing their nests mostly underground. Termites build mounds above ground that can reach impressive heights, with a system of tunnels and chambers that connect the colony.
Are Ants And Termites Harmful To Humans?
While ants and termites may be a nuisance in and around homes, they are generally not harmful to humans. However, termites can cause significant damage to structures if left unchecked. On the other hand, certain ant species can bite or sting, resulting in discomfort or allergic reactions for some individuals.
Conclusion
Understanding the key differences between ants and termites is crucial for effective pest control. By recognizing their distinct characteristics and behaviors, you can make informed decisions when facing infestations. Being able to identify them accurately will help you safeguard your property and maintain a pest-free environment.

I’m MD Tanvir, and I bring years of expertise gained from working closely with pest control companies to the forefront. My journey in the industry has inspired me to launch Bug Battler, a platform aimed at equipping people with the know-how to combat pests autonomously. Through Bug Battler, I aim to empower individuals with practical insights to tackle pest infestations effectively.