Killing all mosquitoes could disrupt ecosystems, impacting pollination and food webs, leading to biodiversity loss. Mosquitoes serve as food sources and pollinators, playing crucial ecological roles.
Completely eradicating mosquitoes may have adverse effects due to their widespread population. Experts consider local elimination possible, but total extermination poses challenges and potential repercussions on the ecosystem. Instead of eradicating all mosquitoes, some propose targeted methods like using bacteria to control mosquito populations.
This approach aims to reduce mosquito numbers without causing widespread ecological imbalances. Considering the complex ecological roles of mosquitoes, the idea of killing all mosquitoes raises ethical and environmental concerns that need careful consideration.
Credit: www.theatlantic.com
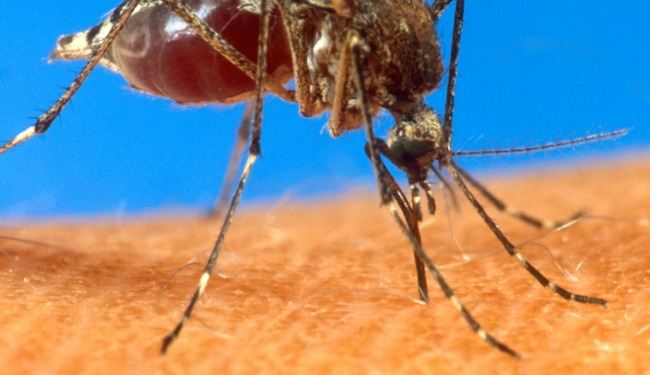
The Mosquito Menace
Mosquitoes, those tiny buzzing insects that seem to always find a way to ruin our outdoor activities, are more than just a nuisance. They pose a significant threat to global health and have earned the title of “The Mosquito Menace”. These tiny pests have the ability to transmit deadly diseases to humans, making them one of the most dangerous creatures on the planet.
Diseases Spread By Mosquitoes
Mosquitoes are responsible for the transmission of various diseases that affect millions of people worldwide. These diseases include:
- Malaria: A life-threatening disease caused by parasites transmitted through the bites of infected mosquitoes. It affects over 200 million people annually and causes hundreds of thousands of deaths.
- Dengue Fever: A viral infection that can cause severe flu-like symptoms, and in some cases, develop into a life-threatening condition known as Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever.
- Zika Virus: An emerging disease that can cause birth defects in infants born to infected mothers and has been linked to neurological disorders in adults.
- Yellow Fever: A viral disease that can cause severe illness and can be fatal. It is endemic in tropical regions of Africa and South America.
- West Nile Virus: A mosquito-borne disease that can cause flu-like symptoms and, in severe cases, neurological complications.
These are just a few examples of the diseases spread by mosquitoes, and the list goes on. The impact of these diseases on global health cannot be underestimated.
Global Health Threats
The diseases transmitted by mosquitoes pose significant global health threats. They not only cause immense suffering and loss of life but also have a severe economic impact on affected countries. The burden of these diseases falls disproportionately on developing nations with limited healthcare resources.
Malaria, for instance, hampers economic development in many African countries, where it is endemic. The high prevalence of the disease leads to increased healthcare costs, decreased productivity, and a weakened workforce. Similarly, outbreaks of dengue fever and Zika virus can overwhelm healthcare systems and strain limited resources.
Moreover, the global spread of these diseases is a constant concern. With increased international travel and climate change, mosquitoes carrying diseases can easily be transported to new regions, potentially causing epidemics in areas previously unaffected.
Addressing the mosquito menace is crucial not only to protect human health but also to safeguard global well-being and promote sustainable development.

Credit: www.cnn.com
Eradication Efforts
While it may seem like a good idea to eradicate all mosquitoes, it’s not that simple. Mosquitoes play an important role in ecosystems as pollinators and as a food source for other wildlife. Complete eradication could have adverse effects and it’s unlikely we could exterminate them all.
Instead, efforts focus on controlling their populations and stopping the spread of diseases they carry through measures like spraying bacteria in their habitats.
Historical Attempts At Control
Throughout history, humans have made various attempts to control mosquito populations. Early methods included the use of natural repellents such as smoke from burning plants and the application of oils to the skin. Additionally, efforts were made to drain swamps and marshes to eliminate mosquito breeding grounds. However, these methods were often ineffective and labor-intensive, resulting in limited success.
Modern Strategies
In modern times, the approach to mosquito control has evolved significantly. The use of insecticides, biological control agents, and genetic modification techniques has become more prominent. Insecticides are commonly applied to stagnant water bodies and areas with high mosquito activity to reduce breeding populations. Biological control methods involve the introduction of natural predators and parasites to limit mosquito numbers. Furthermore, genetic modification techniques aim to alter mosquito genetics to reduce their ability to transmit diseases.
Ecological Role Of Mosquitoes
While mosquitoes may seem like a nuisance to humans, they actually play an important ecological role. Mosquitoes serve as pollinators and a food source for other wildlife, and their elimination could potentially disrupt ecosystems and lead to changes in plant reproduction and food webs.
Therefore, it is important to consider the potential adverse effects before attempting to completely eradicate them.
Pollination And Biodiversity
Mosquitoes play a crucial role in pollination, transferring pollen from one plant to another. This process is essential for the reproduction and genetic diversity of plant species. Without mosquitoes, many plants would struggle to reproduce, leading to a decline in biodiversity.Food Source For Wildlife
Mosquitoes serve as a vital food source for various wildlife species such as birds, bats, fish, and amphibians. Eliminating mosquitoes could disrupt the food chain, impacting the survival of these animals.Mosquitoes are not just pesky insects; they are integral to the functioning of ecosystems. Their removal could have far-reaching consequences on the delicate balance of nature.Consequences Of Extinction
While the idea of eradicating mosquitoes might seem appealing, it is crucial to consider the potential consequences of such an action. Mosquitoes play a significant role in ecosystems, and their extinction could have far-reaching effects on biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
Impact On Ecosystems
Mosquitoes serve as more than just irritating pests. In their aquatic stage, they act as a vital food source for fish and predatory insects. Additionally, mosquitoes function as filter feeders, contributing to the turnover of organic matter in the ecosystem. Their ability to convert organic matter plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of nutrients within the ecosystem.
Without mosquitoes, the absence of their larvae as a food source could disrupt the delicate balance of predator-prey relationships. This disruption could have cascading effects throughout the entire food web, leading to imbalances and potential population declines in other species.
Cascading Effects On Biodiversity
The extinction of mosquitoes could have significant implications for biodiversity. Many species rely on mosquitoes as a crucial food source, including birds, bats, amphibians, and other insects. The loss of mosquitoes could result in a decline in these populations, affecting the overall biodiversity of an ecosystem.
Furthermore, mosquitoes also play a role in plant reproduction. Some species of mosquitoes act as pollinators, helping to fertilize plants and contribute to their reproductive success. The absence of mosquitoes could disrupt this crucial ecological process, potentially impacting the abundance and diversity of plant species.
Considering the interconnectedness of ecosystems, it is essential to carefully evaluate the potential consequences before considering the complete eradication of mosquitoes. While they may be a nuisance to humans, their ecological roles and contributions cannot be overlooked.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations arise when contemplating the idea of killing all mosquitoes. While they may be a nuisance to humans, mosquitoes serve as a vital food source for fish and predatory insects during their aquatic stage. Additionally, their role as pollinators and their impact on the ecosystem make their complete eradication a complex and potentially harmful endeavor.
Moral Dilemmas
When it comes to the topic of killing all mosquitoes, there are many moral dilemmas to consider. While it may seem like a simple solution to eradicate the pesky insects, doing so could have unintended consequences. Mosquitoes may be a nuisance to humans, but they also serve as a food source for other animals and play a role in pollination. Additionally, some argue that all life has inherent value and that it is not our place to decide which species should live or die.Responsibility Towards Nature
As humans, we have a responsibility to consider the impact of our actions on the natural world. Eliminating mosquitoes could have far-reaching consequences beyond just the immediate relief of not having to deal with their bites. Mosquitoes are an important part of many ecosystems and their removal could disrupt food chains and alter the balance of nature. It is important to take a holistic approach when considering the eradication of any species and to weigh the potential benefits against the potential risks.In conclusion, while the idea of killing all mosquitoes may seem appealing, it is important to consider the ethical implications and potential consequences before taking action. It is our responsibility to act as responsible stewards of the environment and to consider the impact of our actions on the natural world. By taking a thoughtful and measured approach, we can work towards solutions that benefit both humans and the wider ecosystem.Practical Challenges
Eliminating all mosquitoes poses practical challenges as they play crucial roles in ecosystems. Mosquitoes serve as food sources for fish and insects and contribute to organic matter turnover, impacting biodiversity and ecosystem stability. Complete eradication could disrupt food webs and have cascading effects on the environment.
Feasibility Of Total Eradication
While the idea of eliminating all mosquitoes may seem like a simple solution to the problems they cause, it is not a practical one. The sheer number of mosquitoes in the world, estimated to be in the billions, makes it nearly impossible to eliminate them all. In addition, mosquitoes serve as an important food source for many animals, including fish, birds, and bats. Removing them from the ecosystem could have unintended consequences and disrupt the natural balance.Adaptive Capabilities Of Mosquitoes
Mosquitoes have evolved to adapt to various environments and conditions. They have been able to survive for millions of years, despite efforts to control their populations. Mosquitoes have become resistant to many insecticides, making it difficult to eradicate them. They also have the ability to lay their eggs in different types of water sources and can quickly repopulate in areas where control measures have been taken.Eliminating all mosquitoes presents practical challenges that cannot be ignored. While some species may not play a significant role in the ecosystem, others serve as important pollinators and food sources for other animals. Additionally, mosquitoes are found all over the world, making it difficult to implement eradication efforts on a global scale. Complete eradication could also have unintended consequences, such as disrupting food webs and causing imbalances in the ecosystem.In conclusion, while the idea of eliminating all mosquitoes may seem like a simple solution to the problems they cause, it is not a practical or feasible one. Instead, efforts should be focused on controlling mosquito populations in areas where they pose a significant threat to human health, while also considering their ecological importance.Alternative Solutions
When considering the issue of mosquito-borne diseases and the potential risks associated with eradicating mosquitoes entirely, alternative solutions present themselves as viable options. These solutions aim to address the problem of mosquito-borne illnesses while minimizing the potential ecological impact of eliminating mosquitoes from the ecosystem.
Targeted Disease Control
Targeted disease control strategies focus on managing mosquito populations to reduce the transmission of diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus. This approach involves the use of insecticides, larvicides, and mosquito traps in specific areas where disease transmission is a concern. Additionally, community education and awareness programs play a crucial role in preventing mosquito-borne illnesses.
Genetic Modification Approaches
Genetic modification approaches involve altering the genetic makeup of mosquitoes to reduce their ability to transmit diseases or to control their population. One example of this is the use of genetically modified mosquitoes that carry a self-limiting gene, which causes offspring to die before reaching maturity. Another approach is the release of sterile male mosquitoes to reduce the overall population size. These methods aim to disrupt the breeding cycle of mosquitoes and ultimately reduce disease transmission.
The Way Forward
Killing all mosquitoes may seem like a solution to eradicate diseases, but it could disrupt the ecosystem. Mosquitoes play a role in pollination and are a food source for other wildlife. Completely eliminating them could have adverse effects on the environment and biodiversity.
Balancing Human Health With Ecology
As we contemplate the prospect of eradicating mosquitoes, it’s crucial to consider the delicate balance between human health and ecological impact. While mosquitoes pose a significant threat to human health due to the diseases they transmit, they also play a vital role in various ecosystems. Therefore, any strategy to control mosquito populations must carefully weigh the potential benefits for human health against the potential ecological consequences.
Developing Sustainable Strategies
When devising plans to address the mosquito dilemma, it’s imperative to develop sustainable strategies that minimize harm to the environment while effectively controlling mosquito populations. This entails exploring innovative and eco-friendly approaches that target mosquitoes without causing widespread ecological disruption. By prioritizing sustainability, we can mitigate the adverse effects on ecosystems while safeguarding human health.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Don’t We Just Get Rid Of Mosquitoes?
We cannot simply get rid of mosquitoes because they serve as a food source for fish and predatory insects in their aquatic stage. They also play an important role in ecosystems by acting as filter feeders and converting organic matter.
Additionally, mosquitoes are pollinators and a food source for other wildlife. Eliminating mosquitoes could disrupt ecosystems, affecting plant reproduction, food webs, and biodiversity.
Why Can’t We Make Mosquitoes Extinct?
We can’t make mosquitoes extinct because they play a vital role in ecosystems as pollinators and food sources. Additionally, eradicating them could disrupt food webs and biodiversity, impacting the stability of ecosystems.
Are Mosquitoes Completely Useless?
Mosquitoes are not completely useless as they serve as pollinators and food sources for wildlife.
Conclusion
While the idea of eradicating mosquitoes may seem appealing, it could have dire consequences. Mosquitoes play a crucial role in ecosystems as pollinators and food sources. Complete elimination could disrupt the balance of nature, impacting biodiversity and ecosystem stability. It’s a complex ethical dilemma.
Related posts:

I’m MD Tanvir, and I bring years of expertise gained from working closely with pest control companies to the forefront. My journey in the industry has inspired me to launch Bug Battler, a platform aimed at equipping people with the know-how to combat pests autonomously. Through Bug Battler, I aim to empower individuals with practical insights to tackle pest infestations effectively.

