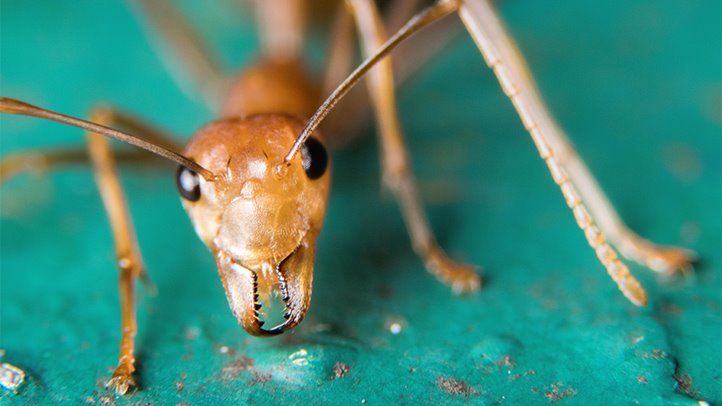
Ant bites involve the injection of formic acid through the insect’s mandibles and sting. This can cause pain, swelling, and redness at the bite site.
Experiencing an ant bite can be an unexpectedly painful ordeal, especially when you unknowingly disturb a well-hidden nest. Ants are equipped with strong mandibles, and some species have a stinger for defense and attack. When an ant bites or stings a person, it releases chemicals like formic acid or venom, leading to a variety of reactions, ranging from mild irritation to severe allergic responses.
These tiny creatures are often underestimated, but their bites serve as a reminder of their survival mechanisms. People frequently seek remedies for ant bites due to their common occurrence in outdoor and even indoor environments. Understanding the biology behind these bites and the potential reactions they can induce is crucial for proper treatment and prevention.

Credit: untamedscience.com
The Fascinating World Of Ants
Welcome to the fascinating world of ants, a realm where these tiny creatures exhibit incredible social behaviors and impact our lives in surprising ways. Ants may appear insignificant at a glance, but their complex society and the way they deal with threats, including how they bite, is nothing short of extraordinary. Let’s delve into the marvel of how ant bites work and discover the intricacies of these ubiquitous insects.
Social Insects With A Sting
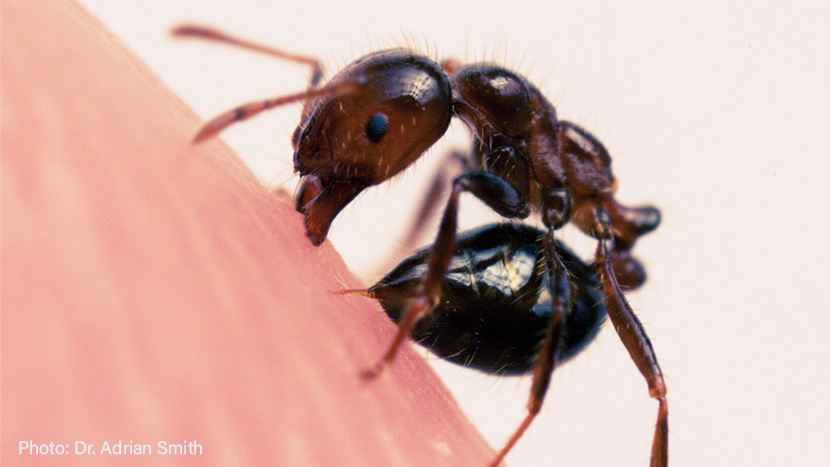
Ants are notorious for their well-organized colonies, each member playing a specific role in their tight-knit community. Worker ants, the ones we commonly encounter, are the colony’s protectors and providers. When they bite, it’s often a defense mechanism to safeguard their home. Some species also inject venom through a stinger, causing discomfort or even allergic reactions in humans and other predators. The process is fascinating: an ant uses its mandibles to grip the skin, then arches its body to insert the stinger and release venom, if it has one.
- Ants communicate and coordinate attacks.
- Some species use stingers to inject venom.
Diverse Species, Diverse Bites
With over 12,000 species of ants across the globe, bite experiences can vary drastically. For instance, the unassuming black garden ant delivers a mild bite, while the harvester ant can cause a more painful sting. The notorious fire ant is well-known for its aggressive biting and stinging behavior, which results in a burning sensation – hence the name. The toxicity of an ant’s sting can be linked to its diet and habitat, influenced by the chemical compounds in its venom.
| Ant Species | Bite Type | Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Black Garden Ant | Bite without venom | Mild discomfort |
| Harvester Ant | Venomous sting | Sharp pain and swelling |
| Fire Ant | Venomous sting | Burning sensation, itching |
Anatomy Behind The Bite
The Anatomy Behind the Bite of an ant reveals complex tools designed for defense and predation. These small creatures can deliver powerful bites and, in some species, a dose of venom. Unraveling the mechanics of an ant’s bite uncovers a world of intricate anatomy and chemical weaponry.
Mandibles: The Biting Mechanism
Ant mandibles function as multipurpose tools. When we zoom in, we notice these aren’t ordinary mouthparts. An ant’s mandibles are hinged, allowing them to open and close with significant force. These tiny but mighty structures are used to:
- Grip prey or objects
- Cut and crush food
- Manipulate items within the nest
- Defend against threats
Ant mandibles work like built-in Swiss Army knives, crucial for survival in the wild.
Venom Apparatus In Ants
Some ant species possess a venom apparatus that intensifies their bite. This arsenal exists beyond the mandibles, in a specialized gland connected to a stinger. Here’s how the venom delivery happens:
- Ant identifies a threat or prey.
- Venom is produced in an internal gland.
- Through muscular contraction, venom travels to the stinger.
- The stinger injects venom into the target.
The venom can immobilize small insects and cause irritation or allergic reactions in larger animals.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Mandibles | Gripping, cutting, crushing, manipulating, defending |
| Venom Gland | Produces venom |
| Stinger | Delivers venom to the target |
Chemistry Of Ant Venom
Ant bites can be more than just an irritating annoyance. They are a sophisticated chemical warfare. The venom that ants inject is a potent cocktail of molecules. It evolved to help them defend their colonies and capture prey. While some ant venoms may only cause mild irritation in humans, others can be more harmful. Understanding the chemistry behind these venoms can be both fascinating and important for treatment.
Formic Acid And Its Effects
Many know that formic acid is the key ingredient in ant venom. It’s named after the Latin word for ant, formica. This simple chemical has a powerful effect:
- Irritation: When ants bite or sting, they release formic acid. This can lead to redness and swelling.
- Pain: The acid can cause a burning sensation. It feels like the sting from a nettle.
Complex Venom Compounds
Aside from formic acid, ant venom contains complex compounds. These compounds vary greatly among different ant species:
| Compound | Effect |
|---|---|
| Alkaloids | Can paralyze or kill small insects |
| Proteins | Trigger allergic reactions in some people |
| Peptides | Can disrupt cell membranes |
The diverse chemistry of ant venom is a testament to their evolutionary success. Some compounds can cause severe allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. It underscores the importance of taking ant bites seriously and seeking treatment when needed.
Mechanics Of An Ant Bite
Understanding an ant bite requires exploring the tiny yet complex system through which ants cause a surprisingly painful sting. Ant bites are more than just a nuisance; they are the result of intricate processes and defenses that ants have evolved over millions of years. This exploration will shed light on the mechanics behind that quick pinch you feel when an ant decides to attack.
The Biting Process
When an ant bites, it uses its mandibles. These are the powerful jaws located at the front of an ant’s face. Ant mandibles are not only for biting; they also serve to carry food, build nests, and protect the colony. Depending on the ant species, the size and strength of the mandibles vary. They can inflict a painful bite as the ant anchors itself to your skin. From there, the real discomfort begins as many ants can also sting.
- Ant locates a threat: It approaches its target.
- Mandibles open: Readies for the bite.
- Sharp pinch: Mandibles clamp down on the skin.
- Anchor mechanism: Ant holds firmly to administer venom.
Injection Of Venom
When certain ants bite, they inject venom. Venom is a chemical cocktail that can cause pain, irritation, and even allergic reactions. This venom comes from a stinger at the end of the ant’s abdomen. Not all ants can sting, but those that do have this specially adapted feature to fend off threats or hunt. When the stinger pierces the skin, venom flows directly into the wound. This rapid injection system is how a tiny ant delivers a powerful message to predators and pesky humans alike.
| Ant Species | Can Sting? | Effects of Venom |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Ant | Yes | Pain, redness, swelling |
| Carpenter Ant | Sometimes | Mild irritation |
| Black Garden Ant | No | Little to no effect |
In conclusion, an ant’s bite is a highly efficient defense mechanism. Next time an ant bites, remember the sophisticated process it uses to deliver that sting!
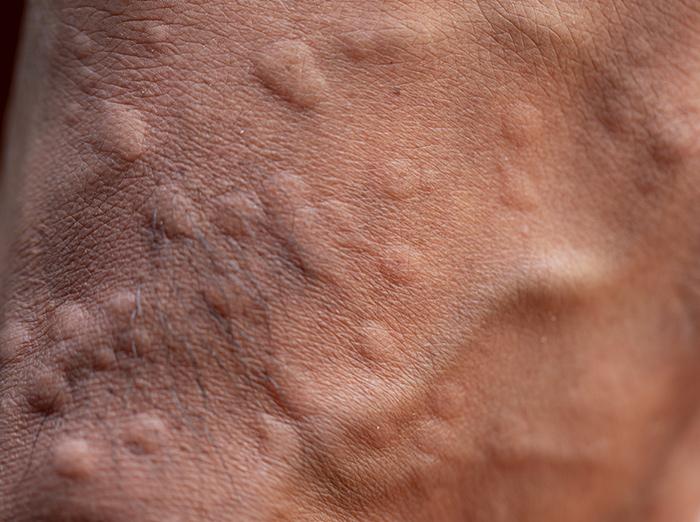
Spotting The Symptoms
Spotting the symptoms of ant bites is essential for timely and effective treatment. When an ant bites, it injects venom that can cause reactions ranging from mild discomfort to severe allergic responses. Knowing what to look out for can help manage the bite and alleviate symptoms quickly.
Immediate Reactions To Ant Bites
- Sharp pain or a stinging sensation
- Redness appearing around the bite area
- Swelling that forms a bump
- Development of a pustule or blister at the bite site
- Itchiness that persists for hours or days
Potential Allergic Responses
Symptoms of an allergic reaction to ant bites can be more serious.
| Symptom | Details |
|---|---|
| Hives | Itchy, raised welts that spread beyond the bite area |
| Difficulty Breathing | Sign of a severe allergic reaction, requires immediate medical attention |
| Swelling of Limbs | Expansion of swelling to other parts of the body |
| Dizziness | A drop in blood pressure can cause faintness or confusion |
| Anaphylaxis | A life-threatening condition that impacts breathing and can cause shock |
If any of these allergic reactions occur, seek medical help promptly.
Treatment Strategies
Ant bites can be painful and sometimes cause allergic reactions. Understanding the right treatment strategies is important for relief and recovery. Let’s explore how to address ant bites effectively.
First Aid Measures
When an ant bites, acting quickly helps reduce discomfort. Follow these steps:
- Wash the area with soap and water to prevent infection.
- Apply a cold compress to reduce swelling and pain.
- Use over-the-counter antihistamines for itching.
- Avoid scratching the bite to prevent skin damage.
When To Seek Medical Help
Most ant bites are harmless, but some cases need a doctor’s care. Look for these signs:
| Symptom | Action |
|---|---|
| Difficulty breathing | Seek immediate medical attention. |
| Swelling in other areas | Consult a doctor promptly. |
| Hives or severe rash | Get medical help without delay. |
| Dizziness or faintness | Call emergency services right away. |
Preventive Measures
Encountering an ant bite can be an uncomfortable and sometimes harmful experience. Taking preventive steps to avoid ant encounters is ideal. By focusing on two key areas, it becomes easier to reduce the risk of ant bites significantly. Let’s explore how you can protect yourself through precautionary measures.
Avoiding Ant Infestations
Keeping ants at bay starts with making your environment less inviting to them. Regular maintenance and cleanliness deter ant infestations. Follow these simple tips:
- Seal cracks and crevices to prevent entry.
- Keep sweet foods in airtight containers.
- Wipe down surfaces to remove crumbs and spills.
- Dispose of garbage promptly and properly.
- Use natural deterrents like vinegar or peppermint oil.
Protective Clothing And Repellents
When entering areas known for ant populations, take extra precautions:
| Clothing | Repellents |
|---|---|
| Wear long sleeves and pants | Apply DEET-based repellents |
| Tuck pants into socks | Use essential oils like lemon eucalyptus |
| Choose light-colored garments | Install ant-repellent devices |
By wearing the right clothing and using repellents, you create a barrier against ant bites.

Credit: www.imperialpestprevent.com
Understanding Ant Behavior
Ants are fascinating creatures. Their world revolves around the colony. They operate as a unit, diligently performing tasks essential for survival. One particular behavior that puzzles many is their tendency to bite. But why do these tiny insects bite, and what can we expect when they interact with us or other animals?
Why Ants Bite
Ants mainly bite for defense or hunting. In defense, biting helps protect the colony from threats. Some ants have stingers to inject venom, enhancing the bite’s effectiveness. When hunting, biting allows ants to subdue prey and carry it back to the nest.
- Defense: Guarding the colony.
- Hunting: Capturing food.
- Venom: Some ants inject venom.
Interactions With Humans And Other Animals
Ants mostly avoid humans. Yet, when nests are disturbed, they may bite in defense. In nature, ants use biting as protection against predators and as a way to compete with other species for resources.
| Interaction | Response |
|---|---|
| Nest Disturbance | Defensive Biting |
| Predators | Bite as Protection |
| Resource Competition | Aggressive Behavior |
Pets can also suffer from ant bites. Reactions to bites vary. They can range from mild irritation to severe discomfort. This depends on the ant species and the animal’s sensitivity.
- Mild irritation.
- Severe discomfort.
Conservation And Coexistence
When we think of ants and their bites, it’s vital to remember our shared environment. Living in harmony with these tiny yet mighty creatures means respecting their space and managing conflicts tactfully. In this section, we will explore the importance of ant habitat conservation and finding a middle ground for human-ant interactions.
Respecting Ant Habitats
Ants play crucial roles in ecosystems, like soil aeration and seed dispersal. Protecting their habitats ensures these benefits continue. Here are several ways to respect their living spaces:
- Avoid disrupting ant hills during outdoor activities.
- Use natural pest control methods, to limit environmental impact.
- Appreciate their ecological role and educate others about it.
Balancing Human-ant Conflicts
At times, ants invade our spaces, leading to potential bites. Here’s how we can balance this conflict:
- Identify ant-friendly zones away from human dwellings.
- Redirect ants using barriers or deterrents.
- Apply gentle relocations for ant colonies when necessary.
Remember, it’s about mutual respect and understanding. Learning to coexist can lead to a healthier planet for all.
Credit: www.millerthekiller.com
Frequently Asked Questions On How Do Ant Bites Work
What Triggers An Ant To Bite?
Ants typically bite when they feel threatened or to defend their colony. The trigger for an ant to bite may be a perceived threat from humans, animals, or other insects encroaching on their territory or disturbing their nest.
Can Ant Bites Be Dangerous?
Most ant bites are not dangerous and cause only minor irritation. However, bites from fire ants, and allergic reactions to any ant bite, can be more severe, requiring medical attention.
How Do Ants Bite And Inject Venom?
Ants bite using their mandibles to grip the skin and then inject venom through a stinger if they are a stinging ant, like a fire ant, or spray formic acid if they lack a stinger, for a painful sensation.
What Are The Symptoms Of An Ant Bite?
Common symptoms include a red bump, mild swelling, pain, itching, and in some cases, a pus-filled blister. Symptoms are usually temporary but can be more intense for sensitive individuals or from venomous species.
Conclusion
Ant bites may be a nuisance, but understanding their mechanics can help prevent and treat them. These tiny creatures pack a punch with their defense tactics. Remember, quick responses to bites limit discomfort. Knowledge and vigilance are key to peacefully coexisting with these industrious insects.
Stay aware, and stay itch-free!

I’m MD Tanvir, and I bring years of expertise gained from working closely with pest control companies to the forefront. My journey in the industry has inspired me to launch Bug Battler, a platform aimed at equipping people with the know-how to combat pests autonomously. Through Bug Battler, I aim to empower individuals with practical insights to tackle pest infestations effectively.

